股票市场趋势预测对于投资者和数据科学家来说都是一个巨大的挑战,因为市场的波动性和复杂性。然而,随着机器学习(ML)的出现,我们可以开发出分析历史数据并预测潜在未来走势的预测模型。在这篇全面的指南中,我们将探讨如何使用Python和机器学习有效地预测股票价格和市场趋势。
1. 问题概述
股票市场受到多种因素的影响,包括:
-
宏观经济指标(如通货膨胀、GDP、失业率)
-
公司基本面(盈利、收入、市盈率)
-
市场情绪(新闻文章、社交媒体活动)
-
技术因素(价格走势、移动平均线、成交量趋势)
股票市场的不确定性很高,没有任何模型能提供完美的预测。然而,通过分析历史价格数据和技术指标,我们可以提取有助于预测未来价格趋势的模式,比如股票在短期或长期内是增加还是减少价值。
2. 收集股市数据
构建预测股票模型的第一个步骤是收集历史股票数据。这些数据可以从金融数据提供商那里轻松获取,例如:
-
Yahoo Finance(通过
yfinancePython包) -
Quandl
-
Alpha Vantage
使用yfinance,你可以下载历史股票数据。让我们获取过去十年苹果公司(AAPL)的数据。
pip install yfinance
import yfinance as yf
# Fetch data for Apple (AAPL) from Yahoo Finance
data = yf.download('AAPL', start='2024-01-01', end='2024-04-01')
print(data.head()) # View the first few rows of the dataset
这些数据包含了一些基本列,如:
-
Open:当天的开盘价
-
High:当天的最高价
-
Low:当天的最低价
-
关闭
:当日收盘价
-
成交量:当日交易股票数量
-
调整后关闭:考虑股息和拆股后的调整收盘价
3. 特征工程
在机器学习中,特征工程至关重要。它涉及从现有数据创建新特征,以增强模型的预测能力。在股票预测中,最常用的特征之一是技术指标。
常见技术指标:
-
简单移动平均(SMA):通过取给定价格集的指定周期数的算术平均值计算得出的移动平均。
-
指数移动平均(EMA):一种加权移动平均,更加重视近期价格数据。
-
相对强度指数(RSI)
:一种动量振荡器,用于衡量价格运动的速率和变化。
-
移动平均收敛发散(MACD):一种趋势跟踪的动量指标,显示股票价格的两个移动平均线之间的关系。
-
布林带:一种波动性指标,包括一个中间带(SMA)和两个外部带(标准差)。
以下是如何在Python中计算这些技术指标的方法:
# Calculate Simple Moving Averages (SMA)
data['SMA_20'] = data['Close'].rolling(window=20).mean()
data['SMA_50'] = data['Close'].rolling(window=50).mean()
# Calculate Exponential Moving Averages (EMA)
data['EMA_20'] = data['Close'].ewm(span=20, adjust=False).mean()
# Calculate Relative Strength Index (RSI)
delta = data['Close'].diff(1)
gain = delta.where(delta > 0, 0)
loss = -delta.where(delta < 0, 0)
avg_gain = gain.rolling(window=14).mean()
avg_loss = loss.rolling(window=14).mean()
rs = avg_gain / avg_loss
data['RSI'] = 100 - (100 / (1 + rs))
# Drop rows with NaN values
data = data.dropna()
包含的技术指标越多,用于训练机器学习模型的数据集就越丰富。然而,请确保所选指标与您的预测任务相关。
4. 为机器学习准备数据集
现在您已经创建了技术指标,接下来您需要通过将数据集分为特征(X)和目标(y)来准备数据集。目标是您想要预测的变量(例如,下一天的收盘价)。以下是设置方法:
# Define the target variable as the next day's closing price
data['Target'] = data['Close'].shift(-1)
# Drop the last row, which has NaN in the 'Target' column
data = data.dropna(subset=['Target'])
# Feature set (dropping unnecessary columns)
X = data[['SMA_20', 'SMA_50', 'EMA_20', 'RSI']]
y = data['Target']
# Drop rows with missing values
X = X.dropna()
y = y[X.index] # Ensure target variable aligns with features
首先,将数据分为训练集和测试集,以评估模型的性能:
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Split into training and testing data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
5. 选择和训练机器学习模型
用于股票市场预测的几个机器学习算法包括:
-
线性回归:一种基于变量之间关系的简单预测模型。
-
随机森林:一种能够处理非线性关系并且防止过拟合的通用模型。
-
支持向量机(SVM):适用于分类和回归任务。
-
长短时记忆网络(LSTM):特别适合时间序列数据的神经网络类型。
为了简单起见,让我们从随机森林回归器开始,这是一个强大的集成学习算法:
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# Initialize and train the model
model = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Predict on the test set
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# Evaluate the model using Mean Squared Error (MSE)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Mean Squared Error: {mse}")

6. 模型评估
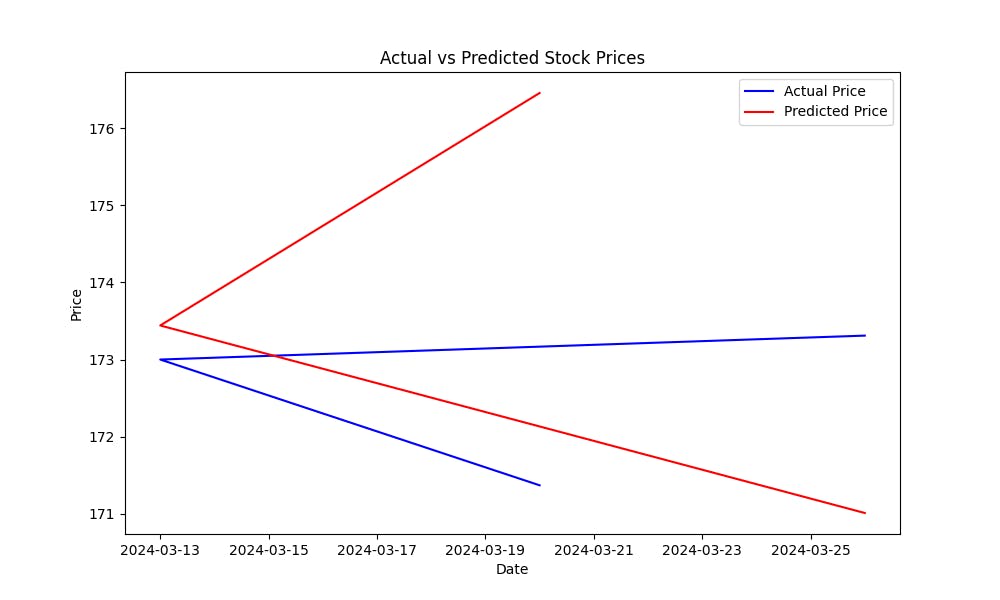
均方误差(MSE) 帮助衡量模型的预测误差。MSE 越低,模型的预测越准确。为了直观地了解模型对股票价格的预测效果,请绘制实际价格与预测价格的对比图:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Plot actual vs predicted prices
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(y_test.index, y_test, label='Actual Price', color='blue')
plt.plot(y_test.index, y_pred, label='Predicted Price', color='red')
plt.title('Actual vs Predicted Stock Prices')
plt.xlabel('Date')
plt.ylabel('Price')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
这幅图将帮助您 visually assess the model’s performance,显示预测值与实际股票价格的接近程度。
完整代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import yfinance as yf
# Fetch data for Apple (AAPL) from Yahoo Finance
data = yf.download('AAPL', start='2024-01-01', end='2024-04-01')
print(data.head()) # View the first few rows of the dataset
# Calculate Simple Moving Averages (SMA)
data['SMA_20'] = data['Close'].rolling(window=20).mean()
data['SMA_50'] = data['Close'].rolling(window=50).mean()
# Calculate Exponential Moving Averages (EMA)
data['EMA_20'] = data['Close'].ewm(span=20, adjust=False).mean()
# Calculate Relative Strength Index (RSI)
delta = data['Close'].diff(1)
gain = delta.where(delta > 0, 0)
loss = -delta.where(delta < 0, 0)
avg_gain = gain.rolling(window=14).mean()
avg_loss = loss.rolling(window=14).mean()
rs = avg_gain / avg_loss
data['RSI'] = 100 - (100 / (1 + rs))
# Drop rows with NaN values (due to moving averages and RSI)
data = data.dropna()
# Define the target variable as the next day's closing price
data['Target'] = data['Close'].shift(-1)
# Drop the last row, which has NaN in the 'Target' column
data = data.dropna(subset=['Target'])
# Feature set (SMA, EMA, RSI)
X = data[['SMA_20', 'SMA_50', 'EMA_20', 'RSI']]
y = data['Target']
# Split into training and testing data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# Initialize and train the model
model = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Predict on the test set
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# Evaluate the model using Mean Squared Error (MSE)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Mean Squared Error: {mse}")
# Plot actual vs predicted prices
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(y_test.index, y_test, label='Actual Price', color='blue')
plt.plot(y_test.index, y_pred, label='Predicted Price', color='red')
plt.title('Actual vs Predicted Stock Prices')
plt.xlabel('Date')
plt.ylabel('Price')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
7. 改进模型
现在您已经建立了一个基本的模型,还有几种方法可以提高其准确性:
-
使用更多特征:包含更多的技术指标、新闻和社交媒体上的情感分析数据,甚至是宏观经济变量。
-
高级机器学习模型:尝试更复杂的算法,如 XGBoost、Gradient Boosting Machines (GBM) 或针对时间序列数据表现更好的深度学习模型如 LSTM。
-
超参数调整:使用 GridSearchCV 或 RandomSearchCV 等技术优化模型参数,以找到最佳的模型配置。
-
特征选择:使用 递归特征消除 (RFE) 等技术,识别对预测贡献最大的特征。
Conclusion
通过持续优化模型、引入更多数据以及尝试不同算法,可以提高股票市场趋势预测模型的预测能力。
下一步
-
尝试更多技术指标和数据来源。
-
尝试不同的机器学习算法(例如,深度学习中的 LSTMs)。
-
通过使用历史数据模拟交易,进行回测。
-
根据实际表现的反馈,不断优化模型。
Source:
https://blog.bytescrum.com/how-to-predict-stock-market-trends-with-python-and-machine-learning













