이 튜토리얼에서는 이진 탐색 트리 데이터 구조를 다룰 것입니다. 이진 탐색 트리에서 값 검색, 삽입 및 제거를 위한 함수를 구현할 것입니다. 이러한 작업을 재귀적으로 및 반복적으로 구현할 것입니다.
이진 탐색 트리
A Binary Search tree has the following property:
- 모든 노드는 왼쪽 자식이 항상 부모 노드보다 작아야 합니다.
- 오른쪽 자식은 항상 부모 노드보다 커야 합니다.
다음 섹션에서는 이진 탐색 트리에서 재귀적 및 반복적으로 검색, 삽입 및 삭제하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다. 먼저 이진 트리 데이터 구조를 만들어 봅시다:
public class BinaryTree {
public TreeNode root;
public static class TreeNode {
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public Object data;
public TreeNode(Object data) {
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
}
위의 구현은 이진 탐색 트리가 아닙니다. 트리에 요소를 삽입하는 제한이 없기 때문입니다.
재귀적으로 BST 검색
다음 자바 프로그램은 BST에서 값을 재귀적으로 검색하는 함수를 포함하고 있습니다.
public class SearchInsertRemoveFromTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* Our Example Binary Search Tree
* 10
* 5 20
* 4 8 15 25
*/
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new TreeNode(10);
tree.root.left = new TreeNode(5);
tree.root.right = new TreeNode(20);
tree.root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
tree.root.left.right = new TreeNode(8);
tree.root.right.left = new TreeNode(15);
tree.root.right.right = new TreeNode(25);
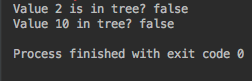
System.out.println("Search Value 2 is in tree? " + searchRecursively(tree.root, 2));
System.out.println("Search Value 10 in tree? " + searchRecursively(tree.root, 10));
}
public static boolean searchRecursively(TreeNode root, int value) {
if (root == null)
return false;
if ((int) root.data == value)
return true;
if (value < (int) root.data)
return searchRecursively(root.left, value);
else if (value > (int) root.data)
return searchRecursively(root.right, value);
return false;
}
}
BST 반복적으로 검색하기
대신 다음 방법을 사용하여 반복적으로 검색합니다:
public static boolean searchIteratively(TreeNode root, int value) {
while (root != null) {
if ((int) root.data == value)
return true;
if (value < (int) root.data)
root = root.left;
else
root = root.right;
}
return false;
}
이제 이진 탐색 트리에 새로운 노드를 삽입하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
BST 재귀적으로 삽입하기
public static TreeNode insertionRecursive(TreeNode root, int value) {
if (root == null)
return new TreeNode(value);
if (value < (int) root.data) {
root.left = insertionRecursive(root.left, value);
} else if (value > (int) root.data) {
root.right = insertionRecursive(root.right, value);
}
return root;
}
public static void printInorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
printInorderTraversal(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
printInorderTraversal(root.right);
}
}
위의 메소드를 main 메소드에서 호출하세요:
tree.root = insertionRecursive(tree.root, 24);
tree.root = insertionRecursive(tree.root, 2);
printInorderTraversal(tree.root);
BST 반복적으로 삽입하기
BST 트리에 노드를 반복적으로 삽입하기 위해 두 개의 포인터를 사용하여 트리를 순회해야합니다.
public static TreeNode insertionIterative(TreeNode root, int value) {
TreeNode current, parent;
TreeNode tempNode = new TreeNode(value);
if (root == null) {
root = tempNode;
return root;
} else {
current = root;
}
while (true) {
parent = current;
if (value < (int) current.data) {
current = current.left;
if (current == null) {
parent.left = tempNode;
return root;
}
} else if (value > (int) current.data) {
current = current.right;
if (current == null) {
parent.right = tempNode;
return root;
}
}
}
}
BST 요소 재귀적으로 제거하기
BST에서 요소를 제거하는 것은 검색과 삽입보다 복잡합니다. BST 속성을 보존해야하기 때문입니다. 노드를 삭제하려면 먼저 해당 노드를 검색해야합니다. 그런 다음 해당 노드에 자식이 있는지 여부를 결정해야합니다.
- 자식이 없는 경우 – 그냥 삭제합니다.
- 하나의 자식이 있는 경우 – 해당 자식을 노드로 복사합니다.
- 두 개의 자식이 있는 경우 – 오른쪽 서브트리에서 다음으로 큰 요소(중위 후속자)를 결정합니다. 제거할 노드를 중위 후속자로 바꿉니다. 중위 후속자의 중복을 삭제합니다.
중위 후속자는 노드의 오른쪽 자식에서 최솟값을 찾아 얻을 수 있습니다.
다음은 BST에서 요소를 제거하는 자바 프로그램입니다:
public static TreeNode deleteRecursively(TreeNode root, int value) {
if (root == null)
return root;
if (value < (int) root.data) {
root.left = deleteRecursively(root.left, value);
} else if (value > (int) root.data) {
root.right = deleteRecursively(root.right, value);
} else {
if (root.left == null) {
return root.right;
} else if (root.right == null)
return root.left;
root.data = inOrderSuccessor(root.right);
root.right = deleteRecursively(root.right, (int) root.data);
}
return root;
}
public static int inOrderSuccessor(TreeNode root) {
int minimum = (int) root.data;
while (root.left != null) {
minimum = (int) root.left.data;
root = root.left;
}
return minimum;
}
main 메서드에서 위의 delete 메서드를 호출합니다:
tree.root = deleteRecursively(tree.root, 4);
tree.root = deleteRecursively(tree.root, 20);
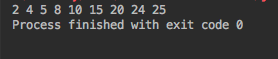
printInorderTraversal(tree.root);
출력은: 2 5 8 10 15 24 25 이제 같은 작업을 반복적으로 수행해 보겠습니다.
BST 반복적으로 요소 제거
public static TreeNode deleteNodeIteratively(TreeNode root, int value) {
TreeNode parent = null, current = root;
boolean hasLeft = false;
if (root == null)
return root;
while (current != null) {
if ((int) current.data == value) {
break;
}
parent = current;
if (value < (int) current.data) {
hasLeft = true;
current = current.left;
} else {
hasLeft = false;
current = current.right;
}
}
if (parent == null) {
return deleteNodeIteratively(current);
}
if (hasLeft) {
parent.left = deleteNodeIteratively(current);
} else {
parent.right = deleteNodeIteratively(current);
}
return root;
}
private static TreeNode deleteNodeIteratively(TreeNode node) {
if (node != null) {
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
return null;
}
if (node.left != null && node.right != null) {
TreeNode inOrderSuccessor = deleteInOrderSuccessorDuplicate(node);
node.data = inOrderSuccessor.data;
} else if (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
} else {
node = node.right;
}
}
return node;
}
private static TreeNode deleteInOrderSuccessorDuplicate(TreeNode node) {
TreeNode parent = node;
node = node.right;
boolean rightChild = node.left == null;
while (node.left != null) {
parent = node;
node = node.left;
}
if (rightChild) {
parent.right = node.right;
} else {
parent.left = node.right;
}
node.right = null;
return node;
}
BST 작업의 시간 복잡도는 O(h)입니다. 여기서 h는 트리의 높이입니다.
이 자습서는 여기서 끝납니다.
전체 코드 및 DS & Algorithm 예제는 GitHub 저장소에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/binary-search-tree-bst-search-insert-remove