在這個教程中,我們將討論二元搜尋樹數據結構。我們將實現搜索、插入和刪除二元搜尋樹中的值的功能。我們將遞歸和迭代地實現這些操作。
二元搜尋樹
A Binary Search tree has the following property:
- 所有節點應該是左子節點始終小於父節點。
- 右子節點始終大於父節點。
在接下來的章節中,我們將看到如何遞歸和迭代地搜索、插入和刪除BST。首先讓我們創建我們的二元樹數據結構:
public class BinaryTree {
public TreeNode root;
public static class TreeNode {
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public Object data;
public TreeNode(Object data) {
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
}
請注意,上面的實現不是二元搜索樹,因為在插入元素到樹中時沒有限制。
遞歸BST搜索
以下Java程序包含了在BST中遞歸搜索值的功能。
public class SearchInsertRemoveFromTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* Our Example Binary Search Tree
* 10
* 5 20
* 4 8 15 25
*/
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new TreeNode(10);
tree.root.left = new TreeNode(5);
tree.root.right = new TreeNode(20);
tree.root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
tree.root.left.right = new TreeNode(8);
tree.root.right.left = new TreeNode(15);
tree.root.right.right = new TreeNode(25);
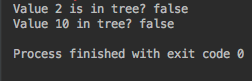
System.out.println("Search Value 2 is in tree? " + searchRecursively(tree.root, 2));
System.out.println("Search Value 10 in tree? " + searchRecursively(tree.root, 10));
}
public static boolean searchRecursively(TreeNode root, int value) {
if (root == null)
return false;
if ((int) root.data == value)
return true;
if (value < (int) root.data)
return searchRecursively(root.left, value);
else if (value > (int) root.data)
return searchRecursively(root.right, value);
return false;
}
}
二元搜尋樹迭代搜尋
為了進行迭代搜尋,請改用以下方法:
public static boolean searchIteratively(TreeNode root, int value) {
while (root != null) {
if ((int) root.data == value)
return true;
if (value < (int) root.data)
root = root.left;
else
root = root.right;
}
return false;
}
讓我們看一下如何在二元搜尋樹中插入新節點。
二元搜尋樹遞歸插入
public static TreeNode insertionRecursive(TreeNode root, int value) {
if (root == null)
return new TreeNode(value);
if (value < (int) root.data) {
root.left = insertionRecursive(root.left, value);
} else if (value > (int) root.data) {
root.right = insertionRecursive(root.right, value);
}
return root;
}
public static void printInorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
printInorderTraversal(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
printInorderTraversal(root.right);
}
}
在主方法中調用上述方法:
tree.root = insertionRecursive(tree.root, 24);
tree.root = insertionRecursive(tree.root, 2);
printInorderTraversal(tree.root);
二元搜尋樹迭代插入
要在二元搜尋樹中迭代插入節點,我們需要使用兩個指針來遍歷樹。
public static TreeNode insertionIterative(TreeNode root, int value) {
TreeNode current, parent;
TreeNode tempNode = new TreeNode(value);
if (root == null) {
root = tempNode;
return root;
} else {
current = root;
}
while (true) {
parent = current;
if (value < (int) current.data) {
current = current.left;
if (current == null) {
parent.left = tempNode;
return root;
}
} else if (value > (int) current.data) {
current = current.right;
if (current == null) {
parent.right = tempNode;
return root;
}
}
}
}
二元搜尋樹遞歸移除元素
刪除二元搜索樹(BST)中的元素比搜索和插入複雜一些,因為我們必須確保保持BST的屬性。要刪除節點,我們首先需要搜索它。然後,我們需要確定該節點是否有子節點。
- 如果沒有子節點 – 直接刪除。
- 如果有一個子節點 – 複製該子節點到該節點。
- 如果有兩個子節點 – 確定右子樹中的中序後繼元素(inorder successor)。用中序後繼元素替換要刪除的節點。刪除中序後繼元素的副本。
中序後繼元素可以通過找到節點的右子樹中的最小值獲得。
以下的Java程序從BST中刪除元素:
public static TreeNode deleteRecursively(TreeNode root, int value) {
if (root == null)
return root;
if (value < (int) root.data) {
root.left = deleteRecursively(root.left, value);
} else if (value > (int) root.data) {
root.right = deleteRecursively(root.right, value);
} else {
if (root.left == null) {
return root.right;
} else if (root.right == null)
return root.left;
root.data = inOrderSuccessor(root.right);
root.right = deleteRecursively(root.right, (int) root.data);
}
return root;
}
public static int inOrderSuccessor(TreeNode root) {
int minimum = (int) root.data;
while (root.left != null) {
minimum = (int) root.left.data;
root = root.left;
}
return minimum;
}
在main方法中調用上述的刪除方法:
tree.root = deleteRecursively(tree.root, 4);
tree.root = deleteRecursively(tree.root, 20);
printInorderTraversal(tree.root);
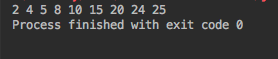
輸出為:2 5 8 10 15 24 25 讓我們以迭代的方式做相同的事情。
以迭代方式刪除BST元素
public static TreeNode deleteNodeIteratively(TreeNode root, int value) {
TreeNode parent = null, current = root;
boolean hasLeft = false;
if (root == null)
return root;
while (current != null) {
if ((int) current.data == value) {
break;
}
parent = current;
if (value < (int) current.data) {
hasLeft = true;
current = current.left;
} else {
hasLeft = false;
current = current.right;
}
}
if (parent == null) {
return deleteNodeIteratively(current);
}
if (hasLeft) {
parent.left = deleteNodeIteratively(current);
} else {
parent.right = deleteNodeIteratively(current);
}
return root;
}
private static TreeNode deleteNodeIteratively(TreeNode node) {
if (node != null) {
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
return null;
}
if (node.left != null && node.right != null) {
TreeNode inOrderSuccessor = deleteInOrderSuccessorDuplicate(node);
node.data = inOrderSuccessor.data;
} else if (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
} else {
node = node.right;
}
}
return node;
}
private static TreeNode deleteInOrderSuccessorDuplicate(TreeNode node) {
TreeNode parent = node;
node = node.right;
boolean rightChild = node.left == null;
while (node.left != null) {
parent = node;
node = node.left;
}
if (rightChild) {
parent.right = node.right;
} else {
parent.left = node.right;
}
node.right = null;
return node;
}
BST操作的時間複雜度為O(h)。其中h是樹的高度。
這就是本教程的結束。
您可以在我們的GitHub存儲庫中查看完整的代碼以及更多的數據結構和算法示例。
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/binary-search-tree-bst-search-insert-remove