このチュートリアルでは、バイナリサーチツリーデータ構造について説明します。バイナリサーチツリーに値を検索、挿入、削除する機能を実装します。これらの操作を再帰的におよび反復的に実装します。
バイナリサーチツリー
A Binary Search tree has the following property:
- すべてのノードは、左の子ノードが常に親ノードより小さくなるようにする必要があります。
- 右の子ノードは常に親ノードより大きくなります。
次のセクションでは、BST内での検索、挿入、削除の再帰的および反復的な方法を見ていきます。まず、バイナリツリーデータ構造を作成しましょう:
public class BinaryTree {
public TreeNode root;
public static class TreeNode {
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public Object data;
public TreeNode(Object data) {
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
}
上記の実装はバイナリサーチツリーではないことに注意してください。ツリーへの要素の挿入に制約がありません。
BSTを再帰的に検索する
次のJavaプログラムには、BST内で値を再帰的に検索する関数が含まれています。
public class SearchInsertRemoveFromTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* Our Example Binary Search Tree
* 10
* 5 20
* 4 8 15 25
*/
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new TreeNode(10);
tree.root.left = new TreeNode(5);
tree.root.right = new TreeNode(20);
tree.root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
tree.root.left.right = new TreeNode(8);
tree.root.right.left = new TreeNode(15);
tree.root.right.right = new TreeNode(25);
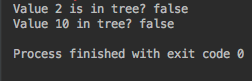
System.out.println("Search Value 2 is in tree? " + searchRecursively(tree.root, 2));
System.out.println("Search Value 10 in tree? " + searchRecursively(tree.root, 10));
}
public static boolean searchRecursively(TreeNode root, int value) {
if (root == null)
return false;
if ((int) root.data == value)
return true;
if (value < (int) root.data)
return searchRecursively(root.left, value);
else if (value > (int) root.data)
return searchRecursively(root.right, value);
return false;
}
}
BSTを反復的に検索する
反復的に検索するには、次の方法を使用します:
public static boolean searchIteratively(TreeNode root, int value) {
while (root != null) {
if ((int) root.data == value)
return true;
if (value < (int) root.data)
root = root.left;
else
root = root.right;
}
return false;
}
新しいノードを二分探索木に挿入する方法を見てみましょう。
BST再帰的挿入
public static TreeNode insertionRecursive(TreeNode root, int value) {
if (root == null)
return new TreeNode(value);
if (value < (int) root.data) {
root.left = insertionRecursive(root.left, value);
} else if (value > (int) root.data) {
root.right = insertionRecursive(root.right, value);
}
return root;
}
public static void printInorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
printInorderTraversal(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
printInorderTraversal(root.right);
}
}
上記のメソッドをメインメソッドで呼び出します:
tree.root = insertionRecursive(tree.root, 24);
tree.root = insertionRecursive(tree.root, 2);
printInorderTraversal(tree.root);
BST反復的挿入
BSTツリーにノードを反復的に挿入するには、2つのポインタを使用してツリーを走査する必要があります。
public static TreeNode insertionIterative(TreeNode root, int value) {
TreeNode current, parent;
TreeNode tempNode = new TreeNode(value);
if (root == null) {
root = tempNode;
return root;
} else {
current = root;
}
while (true) {
parent = current;
if (value < (int) current.data) {
current = current.left;
if (current == null) {
parent.left = tempNode;
return root;
}
} else if (value > (int) current.data) {
current = current.right;
if (current == null) {
parent.right = tempNode;
return root;
}
}
}
}
BST要素の再帰的削除
BSTから要素を削除することは、検索や挿入よりも少し複雑です。BSTの性質が保たれるようにする必要があるからです。ノードを削除するには、まず検索する必要があります。次に、そのノードに子があるかどうかを判断する必要があります。
- 子がない場合 – 単に削除します。
- 単一の子がある場合 – その子をノードにコピーします。
- 2つの子がある場合 – 右のサブツリーで次に高い要素(中間順序の後続要素)を決定します。削除するノードを中間順序の後続要素で置き換えます。中間順序の後続要素の重複を削除します。
中間順序の後続要素は、ノードの右の子の最小値を見つけることで得ることができます。
以下のJavaプログラムは、BSTから要素を削除します:
public static TreeNode deleteRecursively(TreeNode root, int value) {
if (root == null)
return root;
if (value < (int) root.data) {
root.left = deleteRecursively(root.left, value);
} else if (value > (int) root.data) {
root.right = deleteRecursively(root.right, value);
} else {
if (root.left == null) {
return root.right;
} else if (root.right == null)
return root.left;
root.data = inOrderSuccessor(root.right);
root.right = deleteRecursively(root.right, (int) root.data);
}
return root;
}
public static int inOrderSuccessor(TreeNode root) {
int minimum = (int) root.data;
while (root.left != null) {
minimum = (int) root.left.data;
root = root.left;
}
return minimum;
}
上記の削除メソッドをmainメソッドで呼び出します:
tree.root = deleteRecursively(tree.root, 4);
tree.root = deleteRecursively(tree.root, 20);
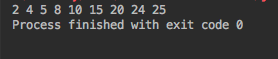
printInorderTraversal(tree.root);
出力は次のとおりです:2 5 8 10 15 24 25同じことを反復的に行いましょう。
BST要素の反復的な削除
public static TreeNode deleteNodeIteratively(TreeNode root, int value) {
TreeNode parent = null, current = root;
boolean hasLeft = false;
if (root == null)
return root;
while (current != null) {
if ((int) current.data == value) {
break;
}
parent = current;
if (value < (int) current.data) {
hasLeft = true;
current = current.left;
} else {
hasLeft = false;
current = current.right;
}
}
if (parent == null) {
return deleteNodeIteratively(current);
}
if (hasLeft) {
parent.left = deleteNodeIteratively(current);
} else {
parent.right = deleteNodeIteratively(current);
}
return root;
}
private static TreeNode deleteNodeIteratively(TreeNode node) {
if (node != null) {
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
return null;
}
if (node.left != null && node.right != null) {
TreeNode inOrderSuccessor = deleteInOrderSuccessorDuplicate(node);
node.data = inOrderSuccessor.data;
} else if (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
} else {
node = node.right;
}
}
return node;
}
private static TreeNode deleteInOrderSuccessorDuplicate(TreeNode node) {
TreeNode parent = node;
node = node.right;
boolean rightChild = node.left == null;
while (node.left != null) {
parent = node;
node = node.left;
}
if (rightChild) {
parent.right = node.right;
} else {
parent.left = node.right;
}
node.right = null;
return node;
}
BST操作の時間計算量はO(h)です。hは木の高さです。
これでチュートリアルは終了です。
完全なコードやその他のデータ構造とアルゴリズムの例については、当社のGitHubリポジトリをご覧ください。
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/binary-search-tree-bst-search-insert-remove