Relu 또는 Rectified Linear Activation Function은 딥 러닝 세계에서 가장 일반적으로 선택되는 활성화 함수입니다. Relu는 최첨단 결과를 제공하며 동시에 계산적으로 매우 효율적입니다.
Relu 활성화 함수의 기본 개념은 다음과 같습니다:
Return 0 if the input is negative otherwise return the input as it is.
수학적으로 다음과 같이 표현할 수 있습니다:
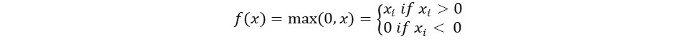
Relu의 의사 코드는 다음과 같습니다:
if input > 0:
return input
else:
return 0
이 튜토리얼에서는 자체 ReLu 함수를 구현하는 방법을 배우고, ReLu의 일부 단점과 더 나은 버전의 ReLu에 대해 배우게 될 것입니다.
추천 독서: 머신 러닝을 위한 선형 대수학 [1/2]
시작해 봅시다!
파이썬에서 ReLu 함수 구현하기
파이썬에서 자체적으로 Relu를 구현해 보겠습니다. 내장된 max 함수를 사용하겠습니다.
Relu의 코드는 다음과 같습니다:
def relu(x):
return max(0.0, x)
함수를 테스트하기 위해 몇 가지 입력에 실행해 보겠습니다.
x = 1.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
완전한 코드
전체 코드는 다음과 같이 주어진다:
def relu(x):
return max(0.0, x)
x = 1.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
출력:
Applying Relu on (1.0) gives 1.0
Applying Relu on (-10.0) gives 0.0
Applying Relu on (0.0) gives 0.0
Applying Relu on (15.0) gives 15.0
Applying Relu on (-20.0) gives 0.0
ReLu 함수의 기울기
ReLu 함수의 기울기(도함수)는 다음과 같다. 미분하면 다음 함수를 얻을 것이다:
f'(x) = 1, x>=0
= 0, x<0
우리는 x가 0보다 작은 값들에 대해 기울기가 0인 것을 볼 수 있다. 이는 일부 뉴런의 가중치와 편향이 업데이트되지 않는 문제가 될 수 있다. 훈련 과정에서 문제가 될 수 있다.
이 문제를 극복하기 위해 우리는 Leaky ReLu 함수를 가지고 있다. 다음에 대해 알아보자.
Leaky ReLu 함수
Leaky ReLu 함수는 일반적인 ReLu 함수의 개선 버전이다. 음수 입력에 대한 기울기가 0인 문제를 해결하기 위해 Leaky ReLu는 음수 입력에 대해 x의 극히 작은 선형 구성 요소를 제공한다.
수학적으로 우리는 Leaky ReLu를 다음과 같이 표현할 수 있다:
f(x)= 0.01x, x<0
= x, x>=0
수학적으로:
- f(x)=1 (x<0)
- (αx)+1 (x≥0)(x)
여기 a는 위에서 사용한 0.01과 같은 작은 상수입니다.
그래픽적으로 표시할 수 있습니다 :
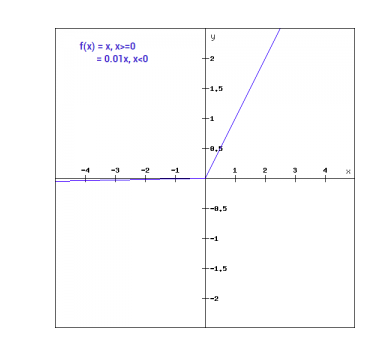
Leaky ReLu의 기울기
Leaky ReLu 함수의 기울기를 계산해 봅시다. 기울기는 다음과 같을 수 있습니다:
f'(x) = 1, x>=0
= 0.01, x<0
이 경우, 음의 입력에 대한 기울기는 0이 아닙니다. 이것은 모든 뉴런이 업데이트될 것을 의미합니다.
Python에서 Leaky ReLu 구현
Leaky ReLu의 구현은 아래와 같습니다 :
def relu(x):
if x>0 :
return x
else :
return 0.01*x
입력값으로 시도해 보겠습니다.
x = 1.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
전체 코드
Leaky ReLu의 전체 코드는 아래와 같습니다 :
def leaky_relu(x):
if x>0 :
return x
else :
return 0.01*x
x = 1.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
출력 :
Applying Leaky Relu on (1.0) gives 1.0
Applying Leaky Relu on (-10.0) gives -0.1
Applying Leaky Relu on (0.0) gives 0.0
Applying Leaky Relu on (15.0) gives 15.0
Applying Leaky Relu on (-20.0) gives -0.2
결론
{
“error”: “Upstream error…”
}
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/relu-function-in-python













