ReluまたはRectified Linear Activation Functionは、ディープラーニングの世界で最も一般的な活性化関数の選択肢です。 Reluは最先端の結果を提供し、同時に計算効率も非常に高いです。
Relu活性化関数の基本的な概念は次のとおりです。
Return 0 if the input is negative otherwise return the input as it is.
数学的には次のように表現できます:
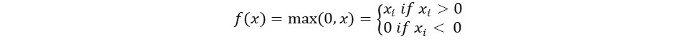
Reluの擬似コードは次のとおりです:
if input > 0:
return input
else:
return 0
このチュートリアルでは、独自のReLu関数を実装する方法を学び、その欠点について学び、ReLuの改良版について学びます。
おすすめの読み物:機械学習のための線形代数[パート1/2]
さあ始めましょう!
PythonでReLu関数を実装する
PythonでReluの独自の実装を書いてみましょう。組み込みのmax関数を使用します。
ReLuのコードは次のとおりです:
def relu(x):
return max(0.0, x)
この関数をテストするために、いくつかの入力で実行してみましょう。
x = 1.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
完全なコード
以下に完全なコードが示されています:
def relu(x):
return max(0.0, x)
x = 1.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
出力:
Applying Relu on (1.0) gives 1.0
Applying Relu on (-10.0) gives 0.0
Applying Relu on (0.0) gives 0.0
Applying Relu on (15.0) gives 15.0
Applying Relu on (-20.0) gives 0.0
ReLu関数の勾配
ReLu関数の勾配(導関数)は次のようになります。微分すると、次の関数が得られます:
f'(x) = 1, x>=0
= 0, x<0
負の値のxに対して、勾配が0であることがわかります。これは、一部のニューロンの重みとバイアスが更新されないことを意味します。トレーニングプロセスで問題が発生する可能性があります。
この問題を克服するために、リーキーReLu関数があります。次にその詳細を学びましょう。
リーキーReLu関数
リーキーReLu関数は、通常のReLu関数の改良版です。負の入力に対する勾配がゼロの問題に対処するために、リーキーReLuは負の入力に対してxの非常に小さな線形成分を与えます。
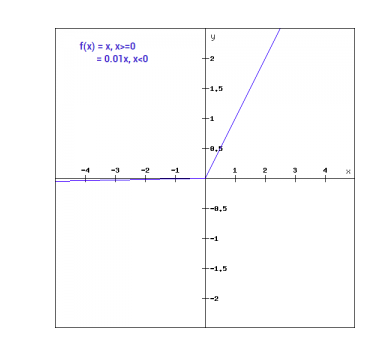
数学的には、リーキーReLuを以下のように表現できます:
f(x)= 0.01x, x<0
= x, x>=0
数学的に:
- f(x)=1 (x<0)
- (αx)+1 (x≧0)(x)
ここにaは、上記の0.01のような小さな定数です。
グラフィカルに示すと、次のようになります:
Leaky ReLuの勾配
Leaky ReLu関数の勾配を計算しましょう。勾配は次のようになります:
f'(x) = 1, x>=0
= 0.01, x<0
この場合、負の入力の勾配はゼロではありません。これは、すべてのニューロンが更新されることを意味します。
PythonでのLeaky ReLuの実装
Leaky ReLuの実装は以下の通りです:
def relu(x):
if x>0 :
return x
else :
return 0.01*x
入力をオンサイトで試してみましょう。
x = 1.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
完全なコード
Leaky ReLuの完全なコードは以下の通りです:
def leaky_relu(x):
if x>0 :
return x
else :
return 0.01*x
x = 1.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
出力:
Applying Leaky Relu on (1.0) gives 1.0
Applying Leaky Relu on (-10.0) gives -0.1
Applying Leaky Relu on (0.0) gives 0.0
Applying Leaky Relu on (15.0) gives 15.0
Applying Leaky Relu on (-20.0) gives -0.2
結論
{
“error”: “Upstream error…”
}
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/relu-function-in-python













