Relu ou Função de Ativação Linear Retificada é a escolha mais comum de função de ativação no mundo do aprendizado profundo. Relu fornece resultados de ponta e é computacionalmente muito eficiente ao mesmo tempo.
O conceito básico da função de ativação Relu é o seguinte:
Return 0 if the input is negative otherwise return the input as it is.
Podemos representá-lo matematicamente da seguinte forma:
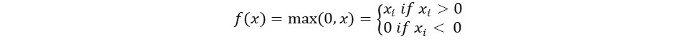
O pseudocódigo para Relu é o seguinte:
if input > 0:
return input
else:
return 0
Neste tutorial, aprenderemos como implementar nossa própria função ReLu, conheceremos algumas de suas desvantagens e aprenderemos sobre uma versão melhorada de ReLu.
Leitura recomendada: Álgebra Linear para Aprendizado de Máquina [Parte 1/2]
Vamos começar!
Implementando a função ReLu em Python
Vamos escrever nossa própria implementação do Relu em Python. Usaremos a função max embutida para implementá-la.
O código para ReLu é o seguinte:
def relu(x):
return max(0.0, x)
Para testar a função, vamos executá-la em algumas entradas.
x = 1.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
Código Completo
O código completo é apresentado abaixo:
def relu(x):
return max(0.0, x)
x = 1.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, relu(x)))
Resultado:
Applying Relu on (1.0) gives 1.0
Applying Relu on (-10.0) gives 0.0
Applying Relu on (0.0) gives 0.0
Applying Relu on (15.0) gives 15.0
Applying Relu on (-20.0) gives 0.0
Gradiente da função ReLu
Vamos ver qual seria o gradiente (derivada) da função ReLu. Ao diferenciar, obtemos a seguinte função:
f'(x) = 1, x>=0
= 0, x<0
Podemos observar que para valores de x menores que zero, o gradiente é 0. Isso significa que os pesos e os vieses para alguns neurônios não são atualizados. Isso pode ser um problema no processo de treinamento.
Para superar esse problema, temos a função Leaky ReLu. Vamos aprender sobre ela a seguir.
Função Leaky ReLu
A função Leaky ReLu é uma improvisação da função ReLu regular. Para lidar com o problema do gradiente zero para valores negativos, o Leaky ReLu atribui uma componente linear extremamente pequena de x para entradas negativas.
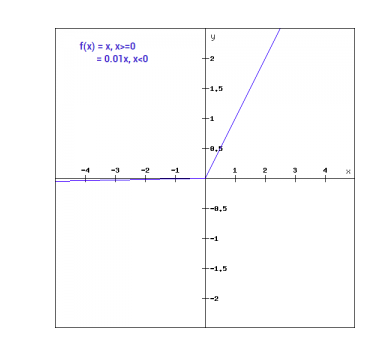
Matematicamente, podemos expressar o Leaky ReLu como:
f(x)= 0.01x, x<0
= x, x>=0
Matematicamente:
- f(x)=1 (x<0)
- (αx)+1 (x≥0)(x)
Aqui está um pequeno constante, assim como o 0.01 que mencionamos anteriormente.
Graficamente, pode ser mostrado como:
O gradiente do Leaky ReLu
Vamos calcular o gradiente para a função Leaky ReLu. O gradiente pode ser calculado como:
f'(x) = 1, x>=0
= 0.01, x<0
Neste caso, o gradiente para entradas negativas é diferente de zero. Isso significa que todos os neurônios serão atualizados.
Implementando o Leaky ReLu em Python
A implementação do Leaky ReLu é mostrada abaixo:
def relu(x):
if x>0 :
return x
else :
return 0.01*x
Vamos experimentar com algumas entradas.
x = 1.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
Código Completo
O código completo para o Leaky ReLu está apresentado abaixo:
def leaky_relu(x):
if x>0 :
return x
else :
return 0.01*x
x = 1.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -10.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 0.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = 15.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
x = -20.0
print('Applying Leaky Relu on (%.1f) gives %.1f' % (x, leaky_relu(x)))
Saída:
Applying Leaky Relu on (1.0) gives 1.0
Applying Leaky Relu on (-10.0) gives -0.1
Applying Leaky Relu on (0.0) gives 0.0
Applying Leaky Relu on (15.0) gives 15.0
Applying Leaky Relu on (-20.0) gives -0.2
Conclusão
Este tutorial foi sobre a função ReLu em Python. Também vimos uma versão aprimorada da função ReLu. O Leaky ReLu resolve o problema dos gradientes zero para valores negativos na função ReLu.
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/relu-function-in-python













