让我们谈谈Python关键字和标识符。最近我们还在这个Python教程中涵盖了一个适用于初学者的安装和设置Python的完整教程。
Python关键字
简而言之,Python关键字是被保留的词汇。这意味着您不能将它们用作任何实体的名称,如变量、类和函数。
所以您可能会想这些关键字有什么用。它们用于定义Python语言的语法和结构。
您应该知道,截至编写本教程时,Python编程语言中有33个关键字。尽管这个数字可能随着时间的推移而变化。另外,Python中的关键字是区分大小写的。因此,它们必须按原样编写。这里是Python编程中所有关键字的列表。
如果您查看所有关键字并试图一次性弄清楚它们,您可能会感到不知所措。因此,现在只需知道这些是关键字。我们将逐个学习它们的用途。您可以通过Python shell的帮助获取Python关键字列表。
所有Python关键字列表
| and | Logical operator |
| as | Alias |
| assert | For debugging |
| break | Break out of Python loops |
| class | Used for defining Classes in Python |
| continue | Keyword used to continue with the Python loop by skipping the existing |
| def | Keyword used for defining a function |
| del | Used for deleting objects in Python |
| elif | Part of the if-elif-else conditional statement in Python |
| else | Same as above |
| except | A Python keyword used to catch exceptions |
| FALSE | Boolean value |
| finally | This keyword is used to run a code snippet when no exceptions occur |
| for | Define a Python for loop |
| from | Used when you need to import only a specific section of a module |
| global | Specify a variable scope as global |
| if | Used for defining an “if” condition |
| import | Python keyword used to import modules |
| in | Checks if specified values are present in an iterable object |
| is | This keyword is used to test for equality. |
| lambda | Create anonymous functions |
| None | The None keyword represents a Null value in PYthon |
| nonlocal | Declare a variable with non-local scope |
| not | Logical operator to negate a condition |
| or | A logical operator used when either one of the conditions needs to be true |
| pass | This Python keyword passes and lets the function continue further |
| raise | Raises an exception when called with the specified value |
| return | Exits a running function and returns the value specified |
| TRUE | Boolean value |
| try | Part of the try…except statement |
| while | Used for defining a Python while loop |
| with | Creates a block to make exception handling and file operations easy |
| yield | Ends a function and returns a generator object |
下面是一个简单的示例,展示了Python程序中if-else的用法。
var = 1;
if(var==1):
print("odd")
else:
print("even")
当我们运行上述程序时,Python通过固定的关键字和语法理解if-else块,然后进行进一步的处理。
什么是Python标识符?
Python标识符是我们赋予变量、函数、类、模块或其他对象的名称。这意味着每当我们想要给实体一个名称时,那就是标识符。
有时变量和标识符经常被误解为相同,但它们并不相同。好吧,为了清晰起见,让我们看看什么是变量?
什么是Python中的变量?
A variable, as the name indicates is something whose value is changeable over time. In fact a variable is a memory location where a value can be stored. Later we can retrieve the value to use. But for doing it we need to give a nickname to that memory location so that we can refer to it. That’s identifier, the nickname.
编写标识符的规则
有一些编写标识符的规则。但首先你必须知道Python是大小写敏感的。这意味着Name和name在Python中是两个不同的标识符。以下是在Python中编写标识符的一些规则。
- 标识符可以是大写字母、小写字母、数字或下划线(_)的组合。因此,myVariable,variable_1,variable_for_print 都是有效的 Python 标识符。
- 标识符不能以数字开头。因此,variable1 是有效的,但 1variable 不是有效的。
- 我们不能在标识符中使用特殊符号如 !、#、@、%、$ 等。
- 标识符的长度可以是任意的。
虽然这些是编写标识符的严格规则,但还有一些命名约定并不是强制性的,而是最好遵循的良好实践。
- 类名以大写字母开头。所有其他标识符以小写字母开头。
- 以单个下划线开头的标识符表示该标识符是私有的。
- 如果标识符以两个下划线开头和结尾,则表示该标识符是语言定义的特殊名称。
- 虽然 c = 10 是有效的,但写成 count = 10 更有意义,而且当您长时间查看代码时,更容易理解它的作用。
- 可以使用下划线分隔多个单词,例如 this_is_a_variable。
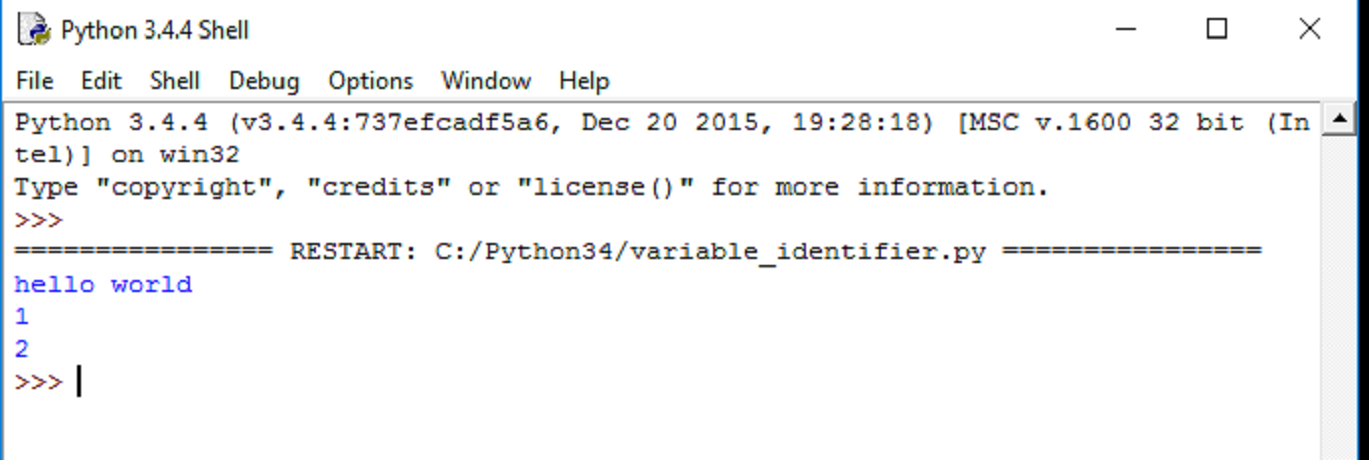
以下是一个 Python 变量的示例程序。
myVariable="hello world"
print(myVariable)
var1=1
print(var1)
var2=2
print(var2)
如果运行该程序,输出将如下图所示。
结论
那么,今天就到这里。在下一个教程中,我们将学习关于Python语句和注释。在那之前,#愉快编码 🙂
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/python-keywords-identifiers














