LLMs need to connect to the real world. LangChain4j tools, combined with Apache Camel, make this easy. Camel provides robust integration, connecting your LLM to any service or API. This lets your AI interact with databases, queues, and more, creating truly powerful applications. We’ll explore this powerful combination and its potential.
Setting Up the Development Environment
- Ollama: Provides a way to run large language models (LLMs) locally. You can run many models, such as LLama3, Mistral, CodeLlama, and many others on your machine, with full CPU and GPU support.
- Visual Studio Code: With Kaoto, Java, and Quarkus plugins installed.
- OpenJDK 21
- Maven
- Quarkus 3.17
- Quarkus Dev Services: A feature of Quarkus that simplifies the development and testing of applications the development and testing of applications that rely on external services such as databases, messaging systems, and other resources.
You can download the complete code at the following GitHub repo.
The following instructions will be executed on Visual Studio Code:
1. Creating the Quarkus Project
mvn io.quarkus:quarkus-maven-plugin:3.17.6:create \
-DprojectGroupId=dev.mikeintoch \
-DprojectArtifactId=camel-agent-tools \
-Dextensions="camel-quarkus-core,camel-quarkus-langchain4j-chat,camel-quarkus-langchain4j-tools,camel-quarkus-platform-http,camel-quarkus-yaml-dsl"2. Adding langchain4j Quarkus Extensions
./mvnw quarkus:add-extension -Dextensions="io.quarkiverse.langchain4j:quarkus-langchain4j-core:0.22.0"
./mvnw quarkus:add-extension -Dextensions="io.quarkiverse.langchain4j:quarkus-langchain4j-ollama:0.22.0"3. Configure Ollama to Run Ollama LLM
Open the application.properties file and add the following lines:
#Configure Ollama local model
quarkus.langchain4j.ollama.chat-model.model-id=qwen2.5:0.5b
quarkus.langchain4j.ollama.chat-model.temperature=0.0
quarkus.langchain4j.ollama.log-requests=true
quarkus.langchain4j.log-responses=true
quarkus.langchain4j.ollama.timeout=180sQuarkus uses Ollama to run LLM locally and also auto wire configuration for the use in Apache camel components in the following steps.
4. Creating Apache Camel Route Using Kaoto
Create a new folder named route in the src/main/resources folder.
Create a new file in the src/main/resources/routes folder and name route-main.camel.yaml, and Visual Studio Code opens the Kaoto visual editor.
Click on the +New button and a new route will be created.
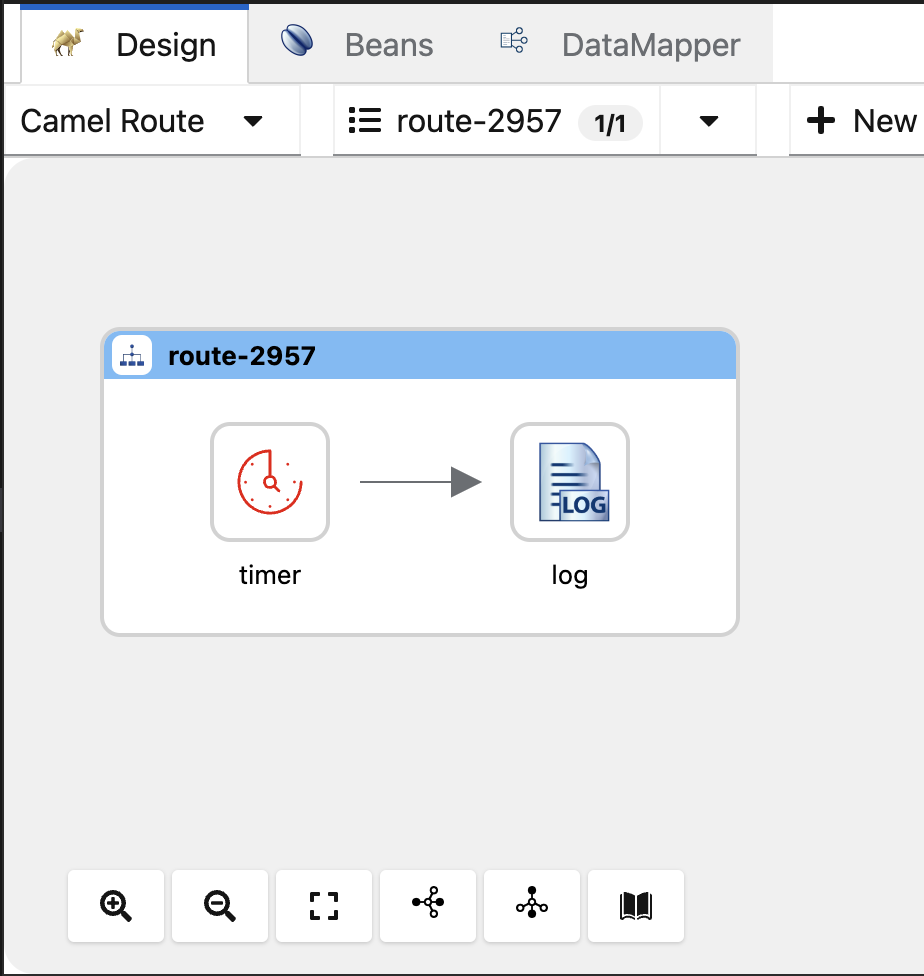
Click on the circular arrows to replace the timer component.
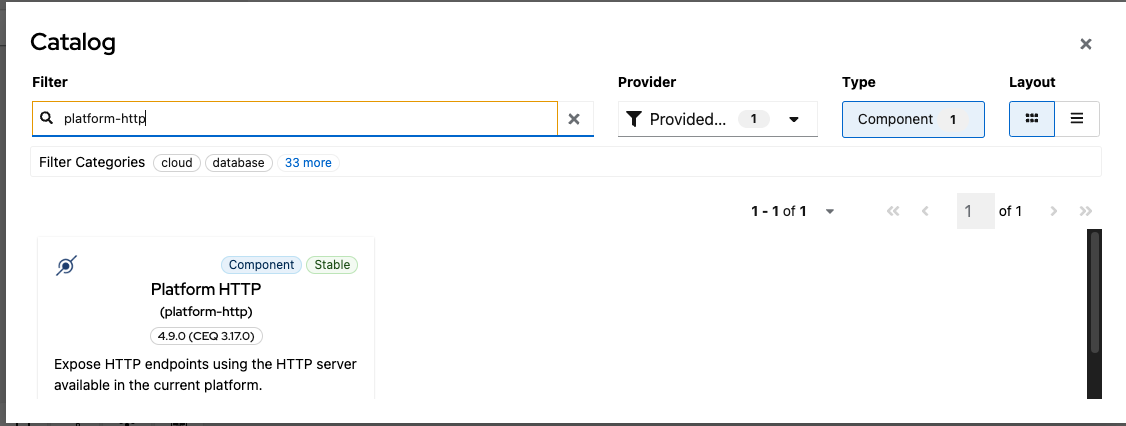
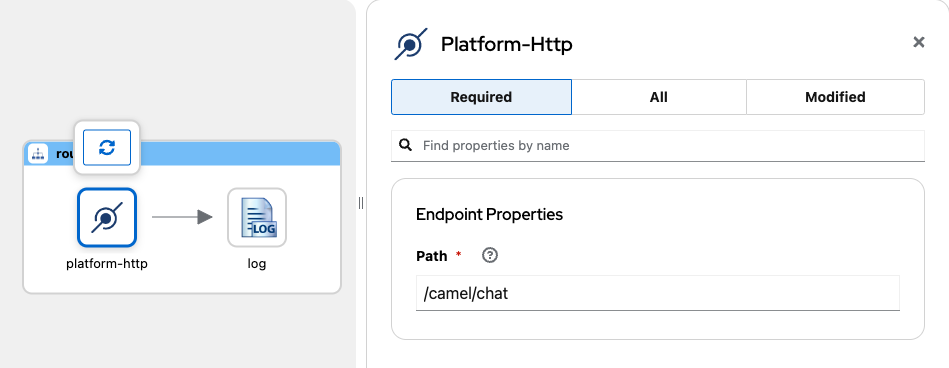
Search and select platform-http component from the catalog.
Configure required platform-http properties:
- Set path with the value /camel/chat
By default, platform-http will be serving on port 8080.
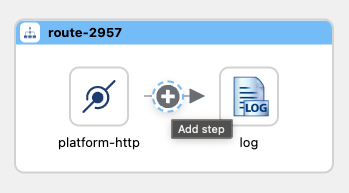
Click on the Add Step Icon in the arrow after the platform-http component.
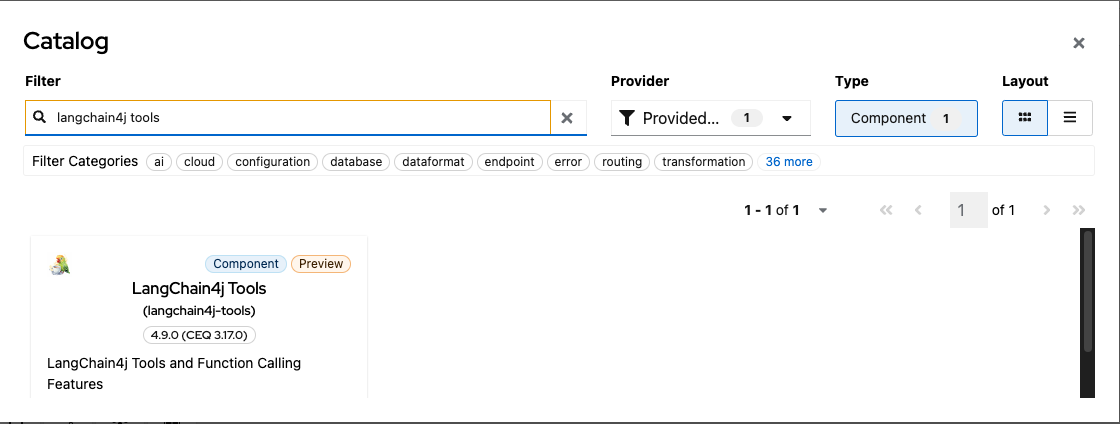
Search and select the langchain4j-tools component in the catalog.
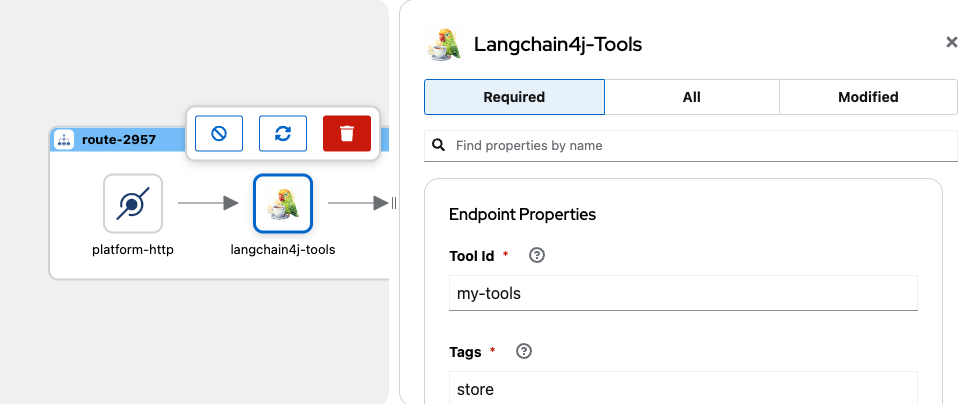
Configure required langchain4j-tools properties:
- Set Tool Id with value my-tools.
- Set Tags with store (Defining tags is for grouping the tools to use with the LLM).
You must process the user input message to the langchain4j-tools component able to use, then click on the Add Step Icon in the arrow after the platform-http component.
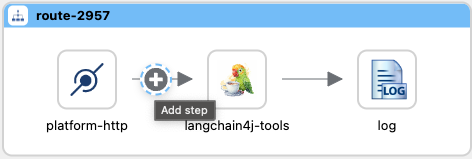
Search and select the Process component in the catalog.
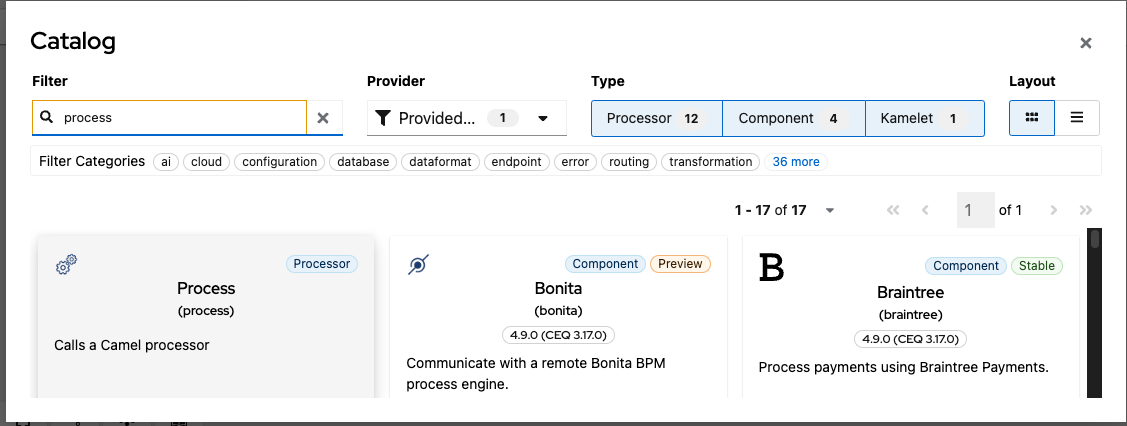
Configure required properties:
- Set Ref with the value createChatMessage.
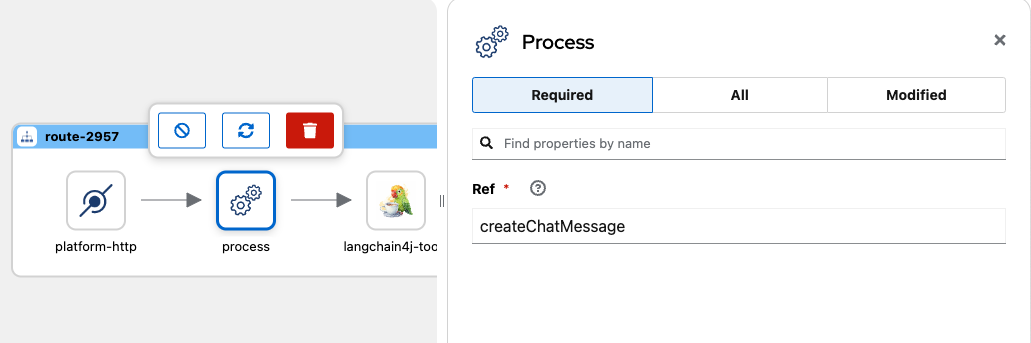
The process component will use the createChatMessage method you will create in the following step.
5. Create a Process to Send User Input to LLM
Create a new Java Class into src/main/java folder named Bindings.java.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import org.apache.camel.BindToRegistry;
import org.apache.camel.Exchange;
import org.apache.camel.Processor;
import org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder;
import dev.langchain4j.data.message.ChatMessage;
import dev.langchain4j.data.message.SystemMessage;
import dev.langchain4j.data.message.UserMessage;
public class Bindings extends RouteBuilder{
@Override
public void configure() throws Exception {
// Routes are loading in yaml files.
}
@BindToRegistry(lazy=true)
public static Processor createChatMessage(){
return new Processor() {
public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception{
String payload = exchange.getMessage().getBody(String.class);
List<ChatMessage> messages = new ArrayList<>();
String systemMessage = """
You are an intelligent store assistant. Users will ask you questions about store product.
Your task is to provide accurate and concise answers.
In the store have shirts, dresses, pants, shoes with no specific category
%s
If you are unable to access the tools to answer the user's query,
Tell the user that the requested information is not available at this time and that they can try again later.
""";
String tools = """
You have access to a collection of tools
You can use multiple tools at the same time
Complete your answer using data obtained from the tools
""";
messages.add(new SystemMessage(systemMessage.formatted(tools)));
messages.add(new UserMessage(payload));
exchange.getIn().setBody(messages);
}
};
}
}This class helps create a Camel Processor to transform the user input into an object that can handle the langchain4j component in the route. It also gives the LLM context for using tools and explains the Agent’s task.
6. Creating Apache Camel Tools for Using With LLM
Create a new file in the src/main/resources/routes folder and name it route-tool-products.camel.yaml, and in Visual Studio Code, open the Kaoto visual editor.
Click on the +New button, and a new route will be created.
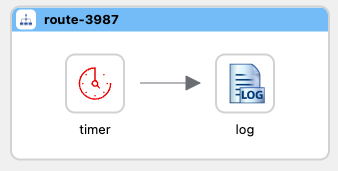
Click on the circular arrows to replace the timer component.
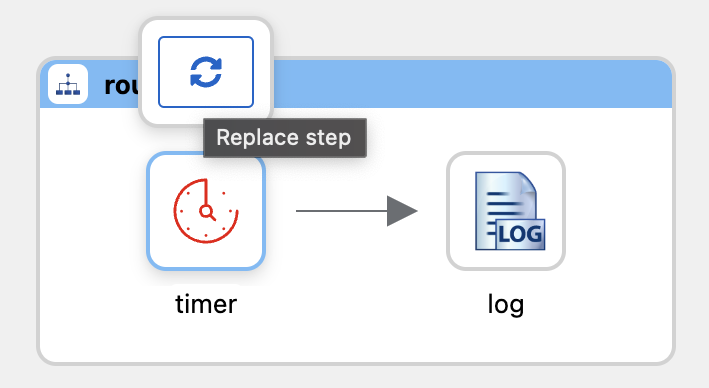
Search and select the langchain4j-tools component in the catalog.
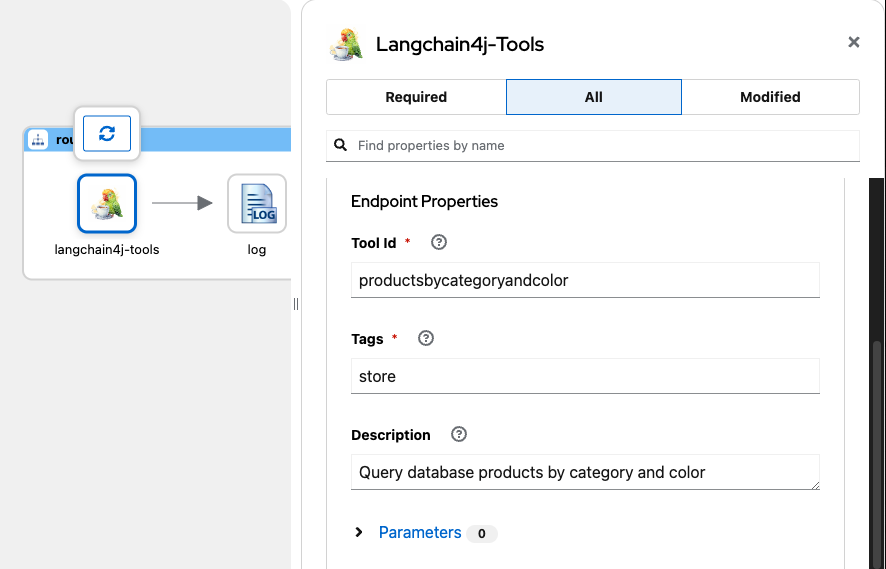
Configure langchain4j-tools, click on the All tab and search Endpoint properties.
- Set Tool Id with value productsbycategoryandcolor.
- Set Tags with store (The same as in the main route).
- Set Description with value Query database products by category and color (a brief description of the tool).
Add parameters that will be used by the tool:
- NAME: category, VALUE: string
- NAME: color, VALUE: string
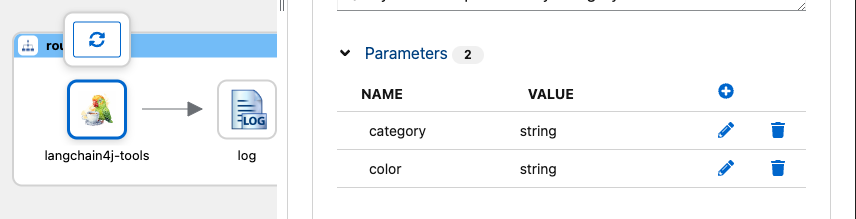
These parameters will be assigned by the LLM for use in the tool and are passed via header.
Add SQL Component to query database, then click on Add Step after the langchain4j-tools component.
Search and select SQL component.
Configure required SQL properties:
- Query with the following value.
Select name, description, category, size, color, price, stock from products where Lower(category)= Lower (:#category) and Lower(color) = Lower(:#color) 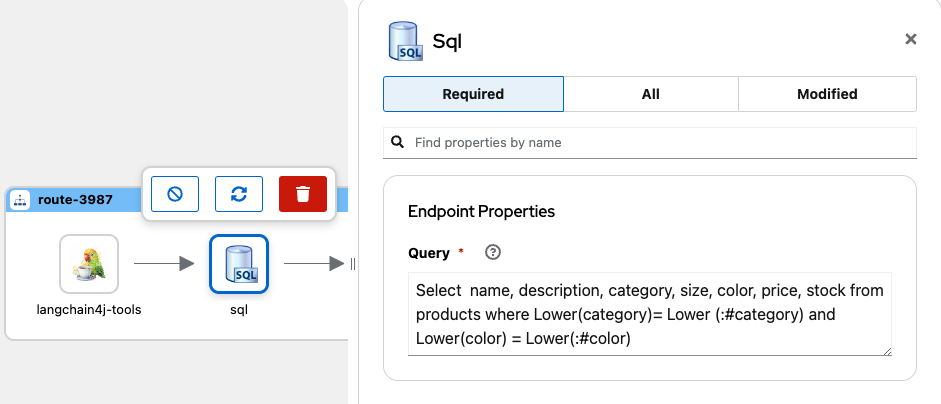
Handle parameters to use in the query, then add a Convert Header component to convert parameters to a correct object type.
Click on the Add Step button after langchain4j-tools, search, and select Convert Header To transformation in the catalog.
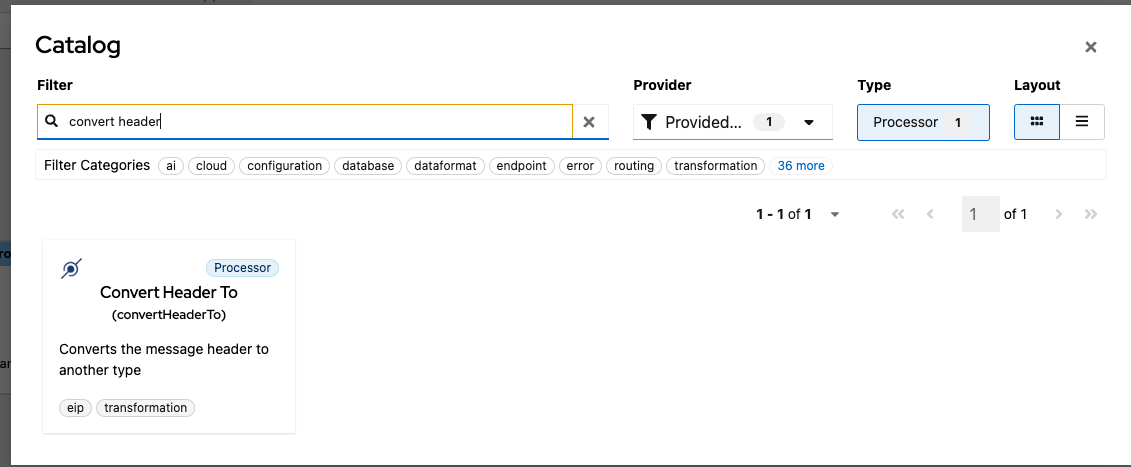
Configure required properties for the component:
- Name with the value category
- Type with the value String
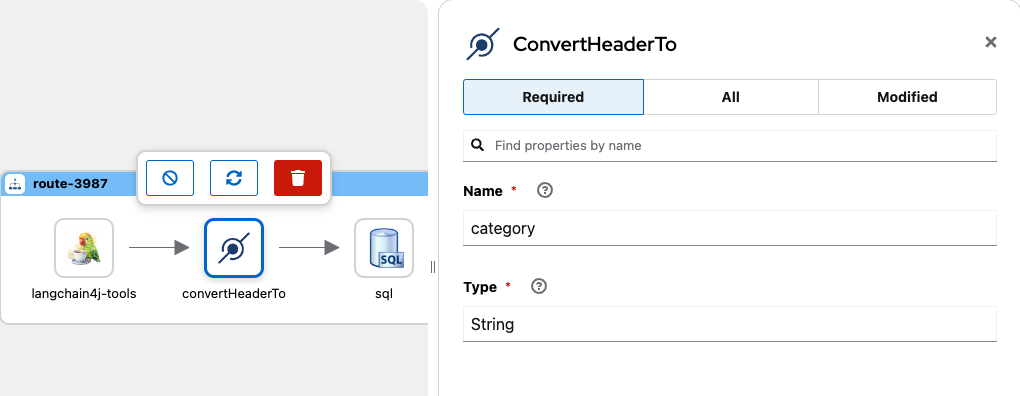
Repeat the steps with the following values:
- Name with the value color
- Type with the value String
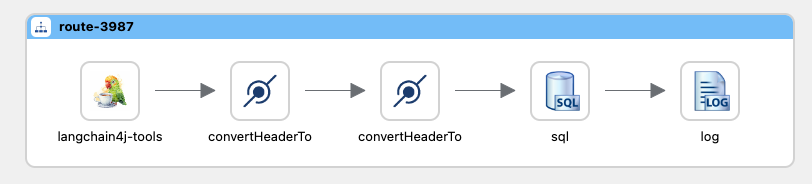
As a result, this is how the route looks like:
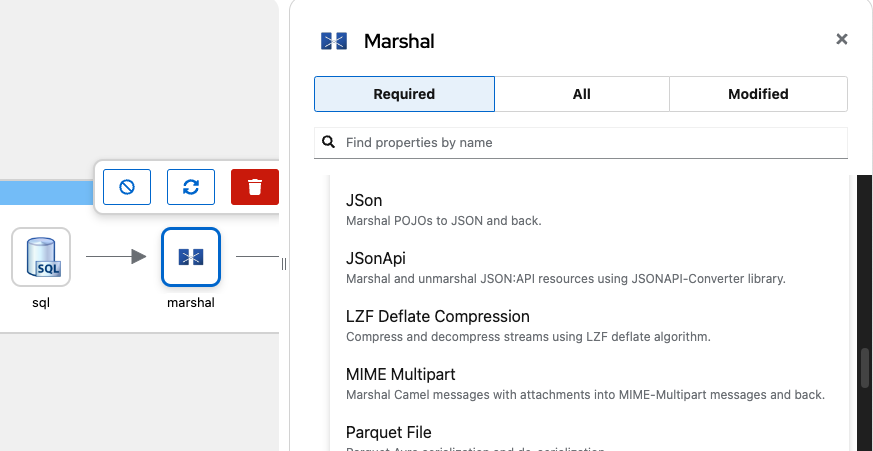
Finally, you need to transform the query result into an object that the LLM can handle; in this example, you transform it into JSON.
Click the Add Step button after SQL Component, and add the Marshal component.

Configure data format properties for the Marshal and select JSon from the list.
7. Configure Quarkus Dev Services for PostgreSQL
Add Quarkus extension to provide PostgreSQL for dev purposes, run following command in terminal.
./mvnw quarkus:add-extension -Dextensions="io.quarkus:quarkus-jdbc-postgresql"Open application.properties and add the following lines:
#Configuring devservices for Postgresql
quarkus.datasource.db-kind=postgresql
quarkus.datasource.devservices.port=5432
quarkus.datasource.devservices.init-script-path=db/schema-init.sql
quarkus.datasource.devservices.db-name=storeFinally, create our SQL script to load the database.
Create a folder named db into src/main/resources, and into this folder, create a file named schema-init.sql with the following content.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS products;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS products (
id SERIAL NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
description varchar(150),
category VARCHAR(50),
size VARCHAR(20),
color VARCHAR(20),
price DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL,
stock INT NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT products_pk PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
INSERT INTO products (name, description, category, size, color, price, stock)
VALUES
('Blue shirt', 'Cotton shirt, short-sleeved', 'Shirts', 'M', 'Blue', 29.99, 10),
('Black pants', 'Jeans, high waisted', 'Pants', '32', 'Black', 49.99, 5),
('White Sneakers', 'Sneakers', 'Shoes', '40', 'White', 69.99, 8),
('Floral Dress', 'Summer dress, floral print, thin straps.', 'Dress', 'M', 'Pink', 39.99, 12),
('Skinny Jeans', 'Dark denim jeans, high waist, skinny fit.', 'Pants', '28', 'Blue', 44.99, 18),
('White Sneakers', 'Casual sneakers, rubber sole, minimalist design.', 'Shoes', '40', 'White', 59.99, 10),
('Beige Chinos', 'Casual dress pants, straight cut, elastic waist.', 'Pants', '32', 'Beige', 39.99, 15),
('White Dress Shirt', 'Cotton shirt, long sleeves, classic collar.', 'Shirts', 'M', 'White', 29.99, 20),
('Brown Hiking Boots', 'Waterproof boots, rubber sole, perfect for hiking.', 'Shoes', '42', 'Brown', 89.99, 7),
('Distressed Jeans', 'Distressed denim jeans, mid-rise, regular fit.', 'Pants', '30', 'Blue', 49.99, 12);8. Include our Route to be Loaded by the Quarkus Project
Camel Quarkus supports several domain-specific languages (DSLs) in defining Camel Routes.
It is also possible to include yaml DSL routes, adding the following line on the application.properties file.
# routes to load
camel.main.routes-include-pattern = routes/*.yamlThis will be load all routes in the src/main/resources/routes folder.
9. Test the App
Run the application using Maven, open a Terminal in Visual Studio code, and run the following command.
mvn quarkus:devOnce it has started, Quarkus calls Ollama and runs your LLM locally, opens a terminal, and verifies with the following command.
ollama ps
NAME ID SIZE PROCESSOR UNTIL
qwen2.5:0.5b a8b0c5157701 1.4 GB 100% GPU 4 minutes from nowAlso, Quarkus creates a container running PostgreSQL and creates a database and schema. You can connect using psql command.
psql -h localhost -p 5432 -U quarkus -d storeAnd query products table:
store=# select * from products;
id | name | description | category | size | color | price | stock
----+--------------------+----------------------------------------------------+----------+------+-------+-------+-------
1 | Blue shirt | Cotton shirt, short-sleeved | Shirts | M | Blue | 29.99 | 10
2 | Black pants | Jeans, high waisted | Pants | 32 | Black | 49.99 | 5
3 | White Sneakers | Sneakers | Shoes | 40 | White | 69.99 | 8
4 | Floral Dress | Summer dress, floral print, thin straps. | Dress | M | Pink | 39.99 | 12
5 | Skinny Jeans | Dark denim jeans, high waist, skinny fit. | Pants | 28 | Blue | 44.99 | 18
6 | White Sneakers | Casual sneakers, rubber sole, minimalist design. | Shoes | 40 | White | 59.99 | 10
7 | Beige Chinos | Casual dress pants, straight cut, elastic waist. | Pants | 32 | Beige | 39.99 | 15
8 | White Dress Shirt | Cotton shirt, long sleeves, classic collar. | Shirts | M | White | 29.99 | 20
9 | Brown Hiking Boots | Waterproof boots, rubber sole, perfect for hiking. | Shoes | 42 | Brown | 89.99 | 7
10 | Distressed Jeans | Distressed denim jeans, mid-rise, regular fit. | Pants | 30 | Blue | 49.99 | 12
(10 rows)To test the app, send a POST request to localhost:8080/camel/chat with a plain text body input. requesting for some product.
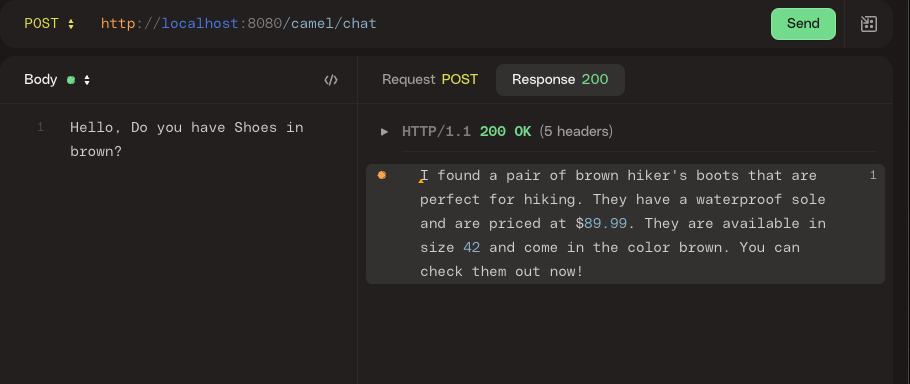
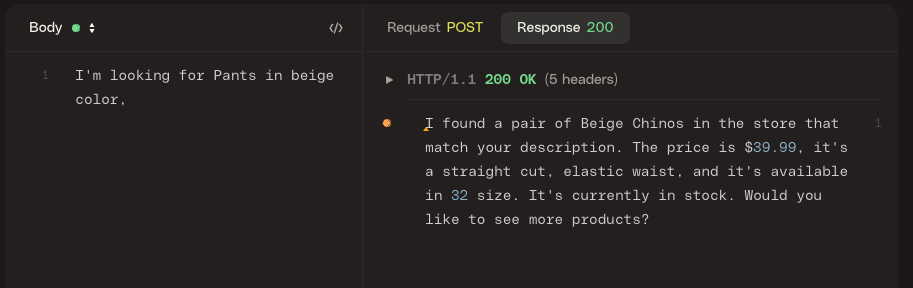
The LLM may have hallucinated. Please try again modifying your request slightly.
You can see how the LLM uses the tool and gets information from the database using the natural language request provided. LLM identifies the parameters and sends them to the tool. If you look in the request log, you can find the tools and parameters LLM is using to create the answer.
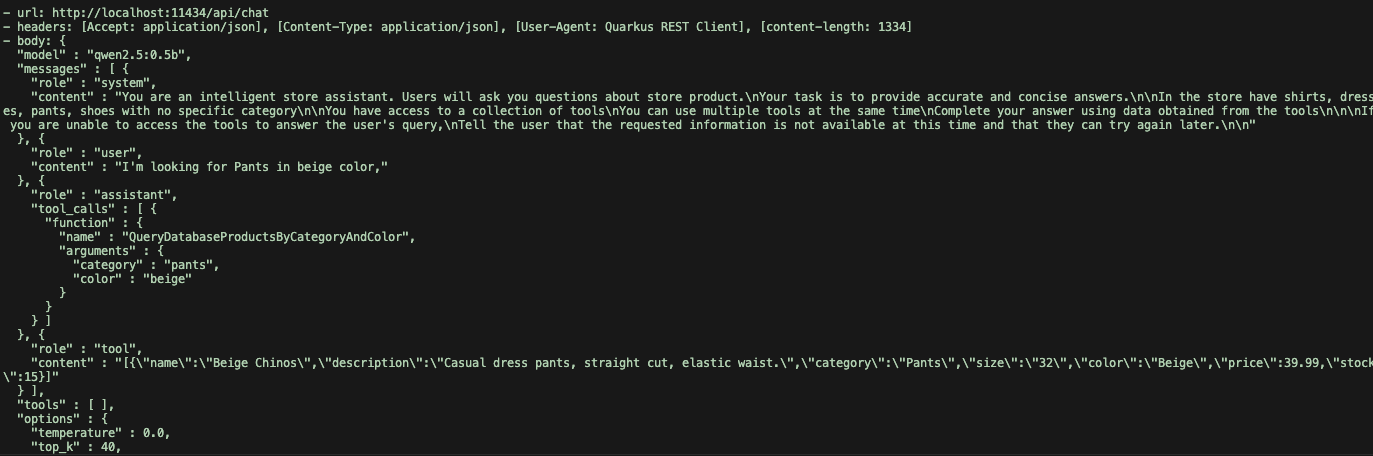
Conclusion
You’ve explored how to leverage the power of LLMs within your integration flows using Apache Camel and the LangChain4j component. We’ve seen how this combination allows you to seamlessly integrate powerful language models into your existing Camel routes, enabling you to build sophisticated applications that can understand, generate, and interact with human language.
Source:
https://dzone.com/articles/powering-llms-with-apache-camel-and-langchain4j













