자, PowerShell 테스트 포트 도구를 구축하는 방법에 대해 알아보겠습니다. 이 도구를 사용하면 포트 번호와 라벨을 사용하여 오픈 포트를 테스트할 수 있습니다.
서버의 절반이 실패하고 멈추지 않는 견고한 스크립트를 만들려면 최종 결과물을 얻기 위한 전제 조건이 충족되는지 먼저 확인하는 것이 중요합니다.
이러한 전제 조건이란 무엇인가요? 전제 조건은 FTP, HTTP, DCOM, WMI, WSMAN 등과 같은 서비스입니다. 서버에 대한 연결은 일반적으로 이러한 서비스와 관련이 있습니다.
연결을 시도하기 전에 서버에서 수행할 수 있는 여러 계층의 확인 작업이 있습니다.
처음에는 네트워크 측면에서 전체 OSI 스택을 횡단해야 합니다. 이는 스크립트를 실행하는 호스트 시스템의 서비스와 원격 호스트 시스템의 모든 기타 사항을 포함하지 않습니다.
원격 서버를 쿼리할 때 수행해야 하는 첫 번째 테스트 중 하나는 적절한 네트워크 포트가 열려 있는지 확인하는 것입니다. 원격 서버에서 실행 중인 서비스에 따라 쿼리해야 할 포트가 다릅니다.
I always used to either not even attempting to test port connections or fumbling around with finding that latest Test-Port script I had scavenged somewhere. Once I found it to figure out what ports I actually needed to a test ahead of time. Today was the final straw.
I needed to query a set of domain controllers before running some CIM queries against them. I went about my normal fumbling around and decided enough was enough and sat down and built my own, fully featured port testing script.
이 Technet 스크립트의 도움을 받아서 TCP 및 UDP 포트를 테스트할 뿐만 아니라 서버 역할별로 포트 그룹을 테스트할 수 있는 좋은 PowerShell 함수 쌍을 만들었습니다. 이제 무슨 서비스가 어떤 포트를 사용하는지 매번 구글링할 필요가 없습니다!
부여됨, 특히 Active Directory의 경우, 포트는 서버 OS, 도메인 컨트롤러의 다양한 서비스 등에 따라 다를 수 있습니다. 환경에 맞게 필요에 따라 조정해 주세요.
여기에 사용 예제의 화면 캡처가 있습니다:
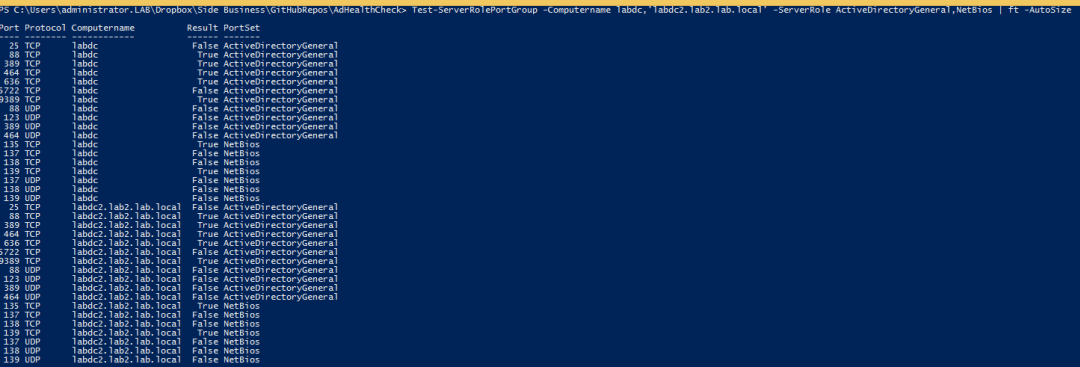
보시다시피, 원하는만큼 많은 서버를 지정할 수 있으며, 각 컴퓨터의 서비스 포트 그룹 및 포트별로 잘 정리된 객체 목록이 출력됩니다. 지금까지 매우 유용하게 사용되었습니다! 제가 사용한 것처럼 여러분도 유용하게 사용하시길 바랍니다!













