Python 비트 연산자는 정수에 대한 비트 연산을 수행하는 데 사용됩니다. 정수는 이진 형식으로 변환되고 비트별 연산이 수행되며, 이로써 비트 연산자라는 이름이 부여됩니다. Python 비트 연산자는 정수에만 작동하며 최종 출력은 10진 형식으로 반환됩니다. Python 비트 연산자는 또한 이진 연산자라고도 불립니다.
Python 비트 연산자
Python에는 6개의 비트 연산자가 있습니다. 아래 표에서 각각에 대한 간략한 정보를 제공합니다.
| Bitwise Operator | Description | Simple Example |
|---|---|---|
| & | Bitwise AND Operator | 10 & 7 = 2 |
| Bitwise OR Operator | ||
| ^ | Bitwise XOR Operator | 10 ^ 7 = 13 |
| ~ | Bitwise Ones’ Compliment Operator | ~10 = -11 |
| << | Bitwise Left Shift operator | 10<<2 = 40 |
| >> | Bitwise Right Shift Operator | 10>>1 = 5 |
이제 이러한 연산자들을 하나씩 살펴보고 어떻게 작동하는지 이해해봅시다.
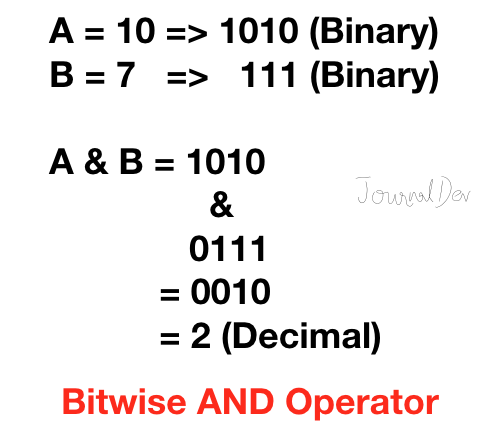
1. 비트 AND 연산자
Python 비트 AND 연산자는 두 비트가 모두 1이면 1을 반환하고, 그렇지 않으면 0을 반환합니다.
>>> 10&7
2
>>>
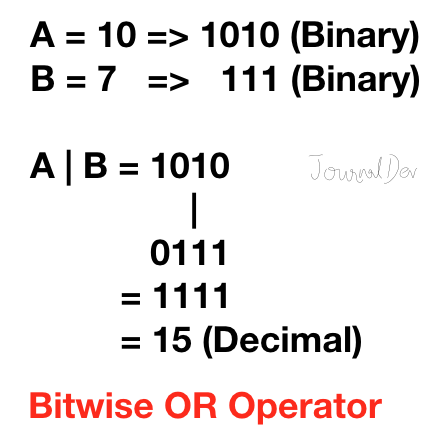
2. 비트 OR 연산자
Python 비트 OR 연산자는 어느 비트라도 1이면 1을 반환합니다. 두 비트가 모두 0이면 0을 반환합니다.
>>> 10|7
15
>>>
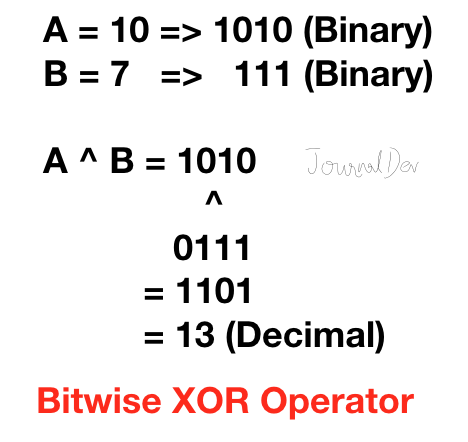
3. 비트 XOR 연산자
파이썬의 비트 XOR 연산자는 한 비트가 0이고 다른 비트가 1이면 1을 반환합니다. 두 비트가 모두 0 또는 1이면 0을 반환합니다.
>>> 10^7
13
>>>
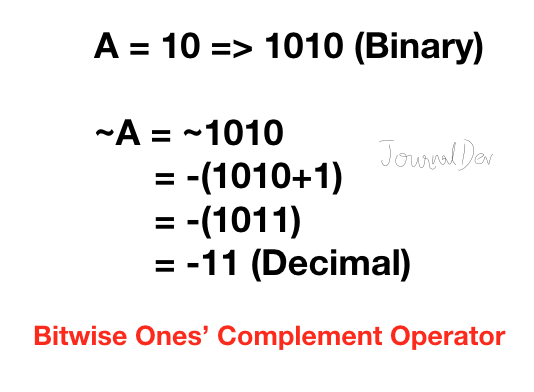
4. 비트 Ones의 보수 연산자
파이썬에서 숫자 ‘A’의 Ones 보수는 -(A+1)과 같습니다.
>>> ~10
-11
>>> ~-10
9
>>>
5. 비트 왼쪽 시프트 연산자
파이썬의 비트 왼쪽 시프트 연산자는 주어진 수만큼 왼쪽 피연산자 비트를 왼쪽으로 이동시킵니다. 간단히 말해, 이진 숫자는 끝에 0을 추가합니다.
>>> 10 << 2
40
>>>

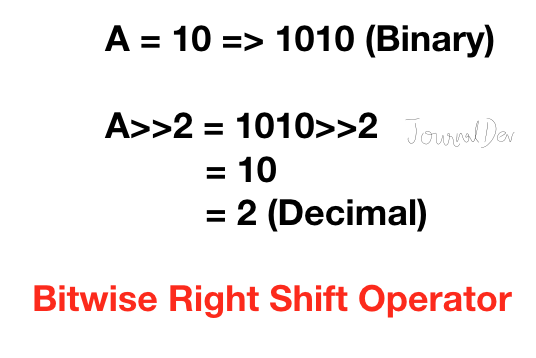
6. 비트 오른쪽 시프트 연산자
파이썬의 오른쪽 시프트 연산자는 왼쪽 시프트 연산자와 정확히 반대입니다. 그럼으로써 왼쪽 피연산자의 비트가 지정된 횟수만큼 오른쪽으로 이동됩니다. 간단하게 말하면 오른쪽 피연산자의 비트가 제거됩니다.
>>> 10 >> 2
2
>>>
파이썬 비트 연산자 오버로딩
파이썬은 연산자 오버로딩을 지원합니다. 사용자 지정 객체에 대한 비트 연산자를 지원하기 위해 구현할 수 있는 여러 가지 방법이 있습니다.
| Bitwise Operator | Method to Implement |
|---|---|
| & | __and__(self, other) |
| ^ | __xor__(self, other) |
| ~ | __invert__(self) |
| << | __lshift__(self, other) |
| >> | __rshift__(self, other) |
다음은 사용자 정의 객체에 대한 비트 연산자 오버로딩의 예입니다.
class Data:
id = 0
def __init__(self, i):
self.id = i
def __and__(self, other):
print('Bitwise AND operator overloaded')
if isinstance(other, Data):
return Data(self.id & other.id)
else:
raise ValueError('Argument must be object of Data')
def __or__(self, other):
print('Bitwise OR operator overloaded')
if isinstance(other, Data):
return Data(self.id | other.id)
else:
raise ValueError('Argument must be object of Data')
def __xor__(self, other):
print('Bitwise XOR operator overloaded')
if isinstance(other, Data):
return Data(self.id ^ other.id)
else:
raise ValueError('Argument must be object of Data')
def __lshift__(self, other):
print('Bitwise Left Shift operator overloaded')
if isinstance(other, int):
return Data(self.id << other)
else:
raise ValueError('Argument must be integer')
def __rshift__(self, other):
print('Bitwise Right Shift operator overloaded')
if isinstance(other, int):
return Data(self.id >> other)
else:
raise ValueError('Argument must be integer')
def __invert__(self):
print('Bitwise Ones Complement operator overloaded')
return Data(~self.id)
def __str__(self):
return f'Data[{self.id}]'
d1 = Data(10)
d2 = Data(7)
print(f'd1&d2 = {d1&d2}')
print(f'd1|d2 = {d1|d2}')
print(f'd1^d2 = {d1^d2}')
print(f'd1<<2 = {d1<<2}')
print(f'd1>>2 = {d1>>2}')
print(f'~d1 = {~d1}')
출력:
Bitwise AND operator overloaded
d1&d2 = Data[2]
Bitwise OR operator overloaded
d1|d2 = Data[15]
Bitwise XOR operator overloaded
d1^d2 = Data[13]
Bitwise Left Shift operator overloaded
d1<<2 = Data[40]
Bitwise Right Shift operator overloaded
d1>>2 = Data[2]
Bitwise Ones Complement operator overloaded
~d1 = Data[-11]
새로운 문자열 포맷에 익숙하지 않다면 파이썬의 f-strings을 읽어보세요.
요약
파이썬 비트 연산자는 주로 수학 계산에서 사용됩니다. 사용자 정의 클래스 구현에 대한 비트 연산자를 지원하기 위해 특정 메서드를 구현할 수 있습니다.
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/python-bitwise-operators













