Dateコマンドは、システムの日付と時刻を設定または表示する外部のbashプログラムです。さまざまなフォーマットオプションも提供されます。Dateコマンドは、すべてのLinuxディストリビューションにデフォルトでインストールされています。
$ which date $ type -a date
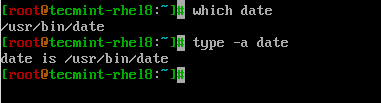
ターミナルでdateコマンドを入力すると、現在の日付と時刻が表示されます。
$ date
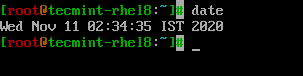
Linuxシステムの日付と時刻を変更する
dateコマンドを使用して、システムの日付、時刻、およびタイムゾーンを変更し、変更をハードウェアクロックと同期する必要があります。
$ date --set="Thu Nov 12 13:06:59 IST 2020" $ hwclock --systohc
フォーマットオプション
A good place to get the list of formatting options will be the man page.
$ man date
使用する一般的なフォーマットオプションのいくつかを見てみましょう。
- フォーマットを適用するには、「+」に続いて「フォーマッタ」を使用します。
- GNU\LINUXのフォーマットオプションのリストを取得するには、リンクされたmanページを参照してください。
- BSDのフォーマットオプションのリストを取得するには、リンクされたmanページを参照してください。
dateコマンドの2つの重要な部分は、フォーマット+%と-dateオプションの使用です。
さて、dateコマンドにいくつかのフォーマットを適用しましょう。フォーマットを適用するには、例に示すようにプラス記号(+)に続いて%formatterを追加します。
Linuxでの日付の取り扱い
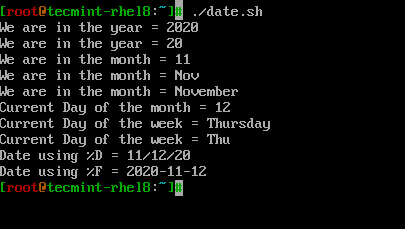
日付関連のフォーマッタを使用する方法を見てみましょう。’date.sh’というシンプルなシェルスクリプトを見てみましょう。
# PRINT YEAR,MONTH,DAY AND DATE... echo "We are in the year = $(date +%Y)" echo "We are in the year = $(date +%y)" # Difference between %Y and %y is %Y will print 4 digits while %y will print the last 2 digits of the year. echo "We are in the month = $(date +%m)" echo "We are in the month = $(date +%b)" echo "We are in the month = $(date +%B)" # Difference between %B and %b is, %B will print full month name while %b will print abbreviated month name. echo "Current Day of the month = $(date +%d)" echo "Current Day of the week = $(date +%A)" echo "Current Day of the week = $(date +%a)" # Difference between %A and %a is, %A will print full Weekday name while %a will print abbreviated weekday name. # Instead of formatting to get the date, we can use %D which will print the date as %m/%d/%y or %F which prints in %Y-%M-%d format. echo "Date using %D = $(date +%D)" echo "Date using %F = $(date +%F)"
Linuxでの時間の取り扱い
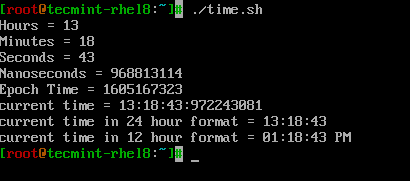
時間関連のフォーマッタを使用する方法を見てみましょう。’time.sh’というシンプルなシェルスクリプトを見てみましょう。
# PRINT HOURS, MINS, SECONDS, NANO SECONDS echo Hours = $(date +%H) echo Minutes = $(date +%M) echo Seconds = $(date +%S) echo Nanoseconds = $(date +%N) echo Epoch Time = $(date +%s) echo "current time = $(date +%H:%M:%S:%N)" # can also use %T which displays Time in HH:MM:SS format. echo "current time in 24 hour format = $(date +%T)" # can also use %r to display time in 12 hour format. echo "current time in 12 hour format = $(date +%r)"
–dateまたは-dフラグで
入力として文字列を渡すと、dateコマンドはそれをスマートに処理できます。
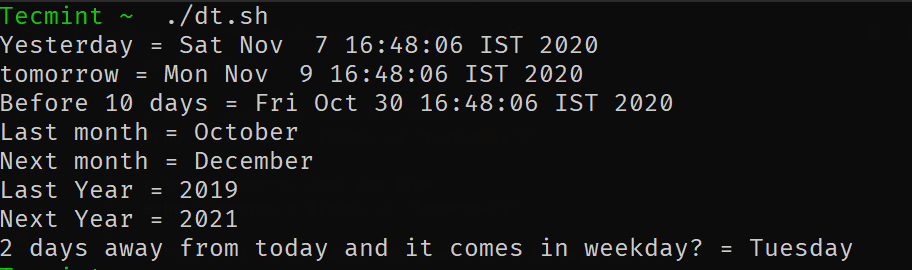
それがどのように機能するかを理解するために、いくつかの例を見てみましょう。
# Print yesterday's date and time. echo "Yesterday = $(date -d "Yesterday")" # Print Tomorrow date and time. echo "tomorrow = $(date -d "tomorrow")" # Find what is the date and time before 10 days from now. echo "Before 10 days = $(date -d "tomorrow -10 days")" # Find last month and next month echo "Last month = $(date -d "last month" "%B")" echo "Next month = $(date -d "next month" "%B")" # Find last year and next year echo "Last Year = $(date -d "last year" "+%Y")" echo "Next Year = $(date -d "next year" "+%Y")" # Forecast the weekday echo "2 days away from today and it comes on weekdays? = $(date -d "Today +2 days" "+%A")
一般的な操作
指定された2つの日付間の日数を計算します。
$ echo $(( ( $(date -d "2020-11-10" "+%s") - $(date -d "2020-11-01" "+%s") ) / 86400))
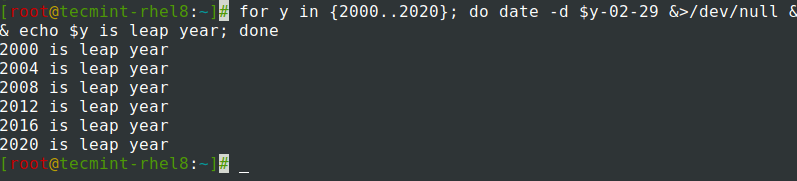
指定された年がうるう年かどうかを調べます。
$ for y in {2000..2020}; do date -d $y-02-29 &>/dev/null && echo $y is leap year; done
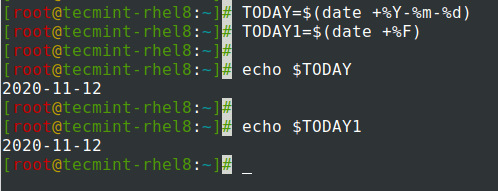
dateコマンドの出力を変数に割り当てます。
$ TODAY=$(date +%Y-%m-%d) OR $ TODAY1=$(date +%F) $ echo $TODAY $ echo $TODAY1
ファイル名に日付を追加してログファイルを作成します。
ログファイル、バックアップ、またはテキストファイルを作成する際に日付と時刻を追加するのはよくある操作です。例を挙げて、バックアップを取るためのシェルスクリプトを作成しました。
このスクリプトは、00:00から23:59までのバックアップを取り、翌日の00:00に毎日スケジュールされて実行されます。昨日の日付形式でログファイルを作成したいです。
CUSTOM_FORMAT=$(date --date "Yesterday" "+%d-%y-%H:%M")
LOG_FILE=/var/log/custom_application/application_${CUSTOM_FORMAT}.log
echo "Script started" >> ${LOG_FILE}
...
CODE BLOCKS
...
echo "Script completed" >> ${LOG_FILE}
これで記事は終わりです。この記事では、Linuxでbashの日付と時刻を使用する方法を紹介しました。ご意見をお聞かせください。
Source:
https://www.tecmint.com/change-linux-system-date-and-time/













