Introduzione
La classe HttpURLConnection del pacchetto java.net può essere utilizzata per inviare una richiesta HTTP Java programmaticamente. In questo articolo, imparerai come utilizzare HttpURLConnection in un programma Java per inviare richieste GET e POST e quindi stampare la risposta.
Prerequisiti
Per questo esempio di HttpURLConnection, dovresti aver completato il Tutorial di Spring MVC perché contiene gli URL per i metodi HTTP GET e POST.
Considera il deployment su un server Tomcat localhost.
Riepilogo di SpringMVCExample
Richiesta HTTP GET in Java
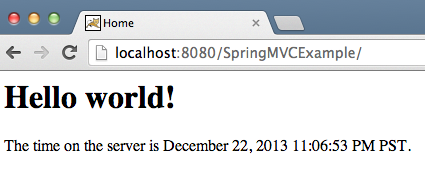
localhost:8080/SpringMVCExample/
Richiesta HTTP GET in Java per la Pagina di Login
localhost:8080/SpringMVCExample/login
Richiesta HTTP POST in Java
localhost:8080/SpringMVCExample?userName=Pankajlocalhost:8080/SpringMVCExample/login?userName=Pankaj&pwd=apple123– per parametri multipli
Estrazione dei parametri dal modulo
L’HTML della pagina di accesso contiene il seguente modulo:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "https://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Login Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="home" method="post">
<input type="text" name="userName"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Login">
</form>
</body>
</html>
- Il
methodèPOST. - L’
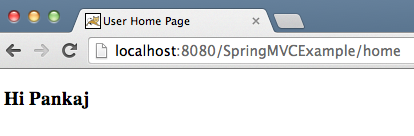
actionèhome.localhost:8080/SpringMVCExample/home
userNameè di tipotext.
È possibile costruire una richiesta POST a:
localhost:8080/SpringMVCExample/home?userName=Pankaj
Questo servirà da base per l’esempio di HttpURLConnection.
Esempio di HttpURLConnection
Ecco i passaggi per inviare richieste HTTP Java utilizzando la classe HttpURLConnection:
- Creare un oggetto
URLdalla stringa URLGEToPOST. - Chiamare il metodo
openConnection()sull’oggetto URL che restituisce un’istanza diHttpURLConnection. - Imposta il metodo di richiesta nell’istanza di
HttpURLConnection(il valore predefinito èGET). - Chiama il metodo
setRequestProperty()sull’istanza diHttpURLConnectionper impostare i valori dell’intestazione della richiesta (come"User-Agent","Accept-Language", ecc.). - Possiamo chiamare
getResponseCode()per ottenere il codice HTTP di risposta. In questo modo, sapremo se la richiesta è stata elaborata con successo o se è stato generato un messaggio di errore HTTP. - Per
GET, utilizzaReadereInputStreamper leggere la risposta e elaborarla di conseguenza. - Per
POST, prima che il codice gestisca la risposta, è necessario ottenere l’OutputStreamdall’istanza diHttpURLConnectione scrivere i parametriPOSTal suo interno.
Ecco un esempio di programma che utilizza HttpURLConnection per inviare richieste Java GET e POST:
package com.journaldev.utils;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
public class HttpURLConnectionExample {
private static final String USER_AGENT = "Mozilla/5.0";
private static final String GET_URL = "https://localhost:9090/SpringMVCExample";
private static final String POST_URL = "https://localhost:9090/SpringMVCExample/home";
private static final String POST_PARAMS = "userName=Pankaj";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
sendGET();
System.out.println("GET DONE");
sendPOST();
System.out.println("POST DONE");
}
private static void sendGET() throws IOException {
URL obj = new URL(GET_URL);
HttpURLConnection con = (HttpURLConnection) obj.openConnection();
con.setRequestMethod("GET");
con.setRequestProperty("User-Agent", USER_AGENT);
int responseCode = con.getResponseCode();
System.out.println("GET Response Code :: " + responseCode);
if (responseCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) { // successo
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(con.getInputStream()));
String inputLine;
StringBuffer response = new StringBuffer();
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(inputLine);
}
in.close();
// stampa il risultato
System.out.println(response.toString());
} else {
System.out.println("GET request did not work.");
}
}
private static void sendPOST() throws IOException {
URL obj = new URL(POST_URL);
HttpURLConnection con = (HttpURLConnection) obj.openConnection();
con.setRequestMethod("POST");
con.setRequestProperty("User-Agent", USER_AGENT);
// Solo per POST - INIZIO
con.setDoOutput(true);
OutputStream os = con.getOutputStream();
os.write(POST_PARAMS.getBytes());
os.flush();
os.close();
// Solo per POST - FINE
int responseCode = con.getResponseCode();
System.out.println("POST Response Code :: " + responseCode);
if (responseCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) { // successo
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(con.getInputStream()));
String inputLine;
StringBuffer response = new StringBuffer();
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(inputLine);
}
in.close();
// stampa il risultato
System.out.println(response.toString());
} else {
System.out.println("POST request did not work.");
}
}
}
Compila ed esegui il codice. Produrrà l’output seguente:
OutputGET Response Code :: 200
<html><head> <title>Home</title></head><body><h1> Hello world! </h1><P> The time on the server is March 6, 2015 9:31:04 PM IST. </P></body></html>
GET DONE
POST Response Code :: 200
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "https://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>User Home Page</title></head><body><h3>Hi Pankaj</h3></body></html>
POST DONE
Confronta questo output con la risposta HTTP del browser.
Se devi inviare richieste GET e POST tramite il protocollo HTTPS, è necessario utilizzare javax.net.ssl.HttpsURLConnection invece di java.net.HttpURLConnection. HttpsURLConnection si occuperà della handshake SSL e della crittografia.
Conclusione
In questo articolo hai appreso come utilizzare HttpURLConnection in un programma Java per inviare richieste GET e POST e successivamente stampare la risposta.
Continua il tuo apprendimento con altri tutorial Java.