Introducción
La clase HttpURLConnection del paquete java.net se puede utilizar para enviar una solicitud HTTP en Java programáticamente. En este artículo, aprenderás cómo utilizar HttpURLConnection en un programa Java para enviar solicitudes GET y POST y luego imprimir la respuesta.
Prerrequisitos
Para este ejemplo de HttpURLConnection, debes haber completado el Tutorial de Spring MVC porque tiene URLs para los métodos HTTP GET y POST.
Considera desplegar en un servidor Tomcat localhost.
Resumen del Ejemplo SpringMVC
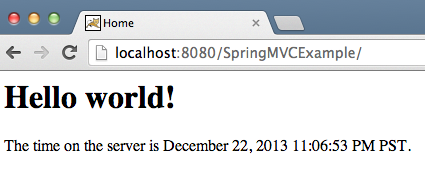
Solicitud HTTP GET en Java
localhost:8080/SpringMVCExample/
Solicitud HTTP GET en Java para la página de inicio de sesión
localhost:8080/SpringMVCExample/login
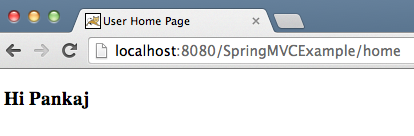
Solicitud HTTP POST en Java
localhost:8080/SpringMVCExample?userName=Pankajlocalhost:8080/SpringMVCExample/login?userName=Pankaj&pwd=apple123– para múltiples parámetros
Derivando parámetros del formulario
El HTML de la página de inicio de sesión contiene el siguiente formulario:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "https://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Login Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="home" method="post">
<input type="text" name="userName"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Login">
</form>
</body>
</html>
- El
methodesPOST. - La
actioneshome.localhost:8080/SpringMVCExample/home
userNamees de tipotext.
Puede construir una solicitud POST a:
localhost:8080/SpringMVCExample/home?userName=Pankaj
Esto servirá como base para el ejemplo de HttpURLConnection.
Ejemplo de HttpURLConnection
Aquí están los pasos para enviar solicitudes HTTP en Java usando la clase HttpURLConnection:
- Crear un objeto
URLa partir de la cadena de URLGEToPOST. - Llamar al método
openConnection()en el objeto URL que devuelve una instancia deHttpURLConnection. - Establezca el método de solicitud en una instancia de
HttpURLConnection(el valor predeterminado esGET). - Llame al método
setRequestProperty()en la instancia deHttpURLConnectionpara establecer los valores de encabezado de la solicitud (como"User-Agent","Accept-Language", etc). - Podemos llamar a
getResponseCode()para obtener el código HTTP de respuesta. De esta manera, sabremos si la solicitud se procesó correctamente o si se lanzó algún mensaje de error HTTP. - Para
GET, useReaderyInputStreampara leer la respuesta y procesarla en consecuencia. - Para
POST, antes de que el código maneje la respuesta, necesita obtener elOutputStreamde la instancia deHttpURLConnectiony escribir los parámetrosPOSTen él.
Aquí hay un ejemplo de programa que utiliza HttpURLConnection para enviar solicitudes Java GET y POST:
package com.journaldev.utils;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
public class HttpURLConnectionExample {
private static final String USER_AGENT = "Mozilla/5.0";
private static final String GET_URL = "https://localhost:9090/SpringMVCExample";
private static final String POST_URL = "https://localhost:9090/SpringMVCExample/home";
private static final String POST_PARAMS = "userName=Pankaj";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
sendGET();
System.out.println("GET DONE");
sendPOST();
System.out.println("POST DONE");
}
private static void sendGET() throws IOException {
URL obj = new URL(GET_URL);
HttpURLConnection con = (HttpURLConnection) obj.openConnection();
con.setRequestMethod("GET");
con.setRequestProperty("User-Agent", USER_AGENT);
int responseCode = con.getResponseCode();
System.out.println("GET Response Code :: " + responseCode);
if (responseCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) { // éxito
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(con.getInputStream()));
String inputLine;
StringBuffer response = new StringBuffer();
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(inputLine);
}
in.close();
// imprimir resultado
System.out.println(response.toString());
} else {
System.out.println("GET request did not work.");
}
}
private static void sendPOST() throws IOException {
URL obj = new URL(POST_URL);
HttpURLConnection con = (HttpURLConnection) obj.openConnection();
con.setRequestMethod("POST");
con.setRequestProperty("User-Agent", USER_AGENT);
// Solo para POST - INICIO
con.setDoOutput(true);
OutputStream os = con.getOutputStream();
os.write(POST_PARAMS.getBytes());
os.flush();
os.close();
// Solo para POST - FIN
int responseCode = con.getResponseCode();
System.out.println("POST Response Code :: " + responseCode);
if (responseCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) { // éxito
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(con.getInputStream()));
String inputLine;
StringBuffer response = new StringBuffer();
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(inputLine);
}
in.close();
// imprimir resultado
System.out.println(response.toString());
} else {
System.out.println("POST request did not work.");
}
}
}
Compile y ejecute el código. Producirá la siguiente salida:
OutputGET Response Code :: 200
<html><head> <title>Home</title></head><body><h1> Hello world! </h1><P> The time on the server is March 6, 2015 9:31:04 PM IST. </P></body></html>
GET DONE
POST Response Code :: 200
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "https://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>User Home Page</title></head><body><h3>Hi Pankaj</h3></body></html>
POST DONE
Compare esta salida con la respuesta HTTP del navegador.
Si tienes que enviar solicitudes GET y POST a través del protocolo HTTPS, entonces necesitas usar javax.net.ssl.HttpsURLConnection en lugar de java.net.HttpURLConnection. HttpsURLConnection manejará el handshake SSL y la encriptación.
Conclusión
En este artículo, aprendiste cómo usar HttpURLConnection en un programa Java para enviar solicitudes GET y POST y luego imprimir la respuesta.
Continúa tu aprendizaje con más tutoriales de Java.