Benvenuti all’esempio di tutorial sull’ExpandableListView di Android. In questo tutorial implementeremo una ExpandableListView che viene utilizzata per raggruppare i dati della lista per categorie. È una sorta di menu e sottomenu in una Android ListView.
Android ExpandableListView
Android ExpandableListView è una vista che mostra gli elementi in una lista a due livelli con scorrimento verticale. Si differenzia da una ListView consentendo due livelli che sono gruppi che possono essere facilmente espansi e compressi toccando per visualizzare e i rispettivi elementi figlio. ExpandableListViewAdapter in Android carica i dati negli elementi associati a questa vista. Di seguito sono riportati alcuni metodi importanti utilizzati da questa classe:
- setChildIndicator(Drawable): Questo viene utilizzato per mostrare un indicatore accanto a ciascun elemento che rappresenta lo stato attuale. Se il figlio è l’ultimo figlio per un gruppo, lo stato
state_lastverrà impostato - setGroupIndicator(Drawable): Viene disegnato un indicatore accanto al gruppo che rappresenta il suo stato, cioè espanso o compresso. Se il gruppo è vuoto, lo stato
state_emptyverrà impostato. Se il gruppo è espanso, lo statostate_expandedverrà impostato - getGroupView(): Restituisce la vista per l’intestazione del gruppo di elenchi
- getChildView() : Restituisce la vista per l’elemento figlio della lista
Le interfacce principali implementate da questa classe sono le seguenti :
- ExpandableListView.OnChildClickListener : Viene sovrascritto per implementare il metodo di callback che viene invocato quando viene cliccato un elemento figlio nella lista espansa
- ExpandableListView.OnGroupClickListener : Viene sovrascritto per implementare il metodo di callback che viene invocato quando viene cliccato l’intestazione di un gruppo nella lista espansa
- ExpandableListView.OnGroupCollapseListener : Viene utilizzato per notificare quando un gruppo viene chiuso
- ExpandableListView.OnGroupExpandListener : Viene utilizzato per notificare quando un gruppo viene espanso
Struttura del progetto Android ExpandableListView
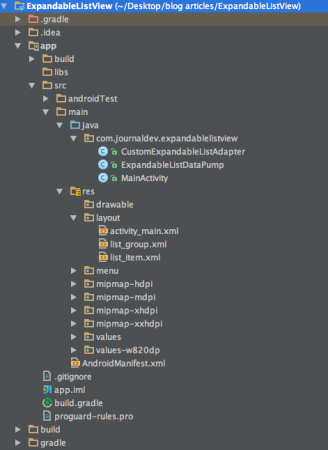 Questo progetto è composto da tre classi.
Questo progetto è composto da tre classi.
- A MainActivity that shows the layout with the ExpandableListView
- Un ExpandableListDataPump che rappresenta dati casuali in una lista e mappa i dati dell’elemento figlio agli intestazioni di gruppo rispettive utilizzando una HashMap
- A CustomExpandableListAdapter which provides the MainActivity with the data from the ExpandableListDataPump class/li>
Codice Android ExpandableListView
L’layout activity_main.xml consiste in un ExpandableListView in un RelativeLayout come mostrato di seguito: activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="https://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<ExpandableListView
android:id="@+id/expandableListView"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:indicatorLeft="?android:attr/expandableListPreferredItemIndicatorLeft"
android:divider="@android:color/darker_gray"
android:dividerHeight="0.5dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
Il android:indicatorLeft è il limite sinistro per l’indicatore degli elementi. Nota: Non possiamo utilizzare il valore wrap_content per l’attributo android:layout_height dell’ ExpandableListView in XML a meno che le dimensioni del genitore siano rigorosamente specificate. Il layout dell’intestazione del gruppo di ogni lista individuale è il seguente: list_group.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/listTitle"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingLeft="?android:attr/expandableListPreferredItemPaddingLeft"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:paddingTop="10dp"
android:paddingBottom="10dp" />
</LinearLayout>
Il layout della riga degli elementi figlio è il seguente: list_item.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/expandedListItem"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingLeft="?android:attr/expandableListPreferredChildPaddingLeft"
android:paddingTop="10dp"
android:paddingBottom="10dp" />
</LinearLayout>
La classe ExpandableListDataPump è definita come segue:
package com.journaldev.expandablelistview;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
public class ExpandableListDataPump {
public static HashMap<String, List<String>> getData() {
HashMap<String, List<String>> expandableListDetail = new HashMap<String, List<String>>();
List<String> cricket = new ArrayList<String>();
cricket.add("India");
cricket.add("Pakistan");
cricket.add("Australia");
cricket.add("England");
cricket.add("South Africa");
List<String> football = new ArrayList<String>();
football.add("Brazil");
football.add("Spain");
football.add("Germany");
football.add("Netherlands");
football.add("Italy");
List<String> basketball = new ArrayList<String>();
basketball.add("United States");
basketball.add("Spain");
basketball.add("Argentina");
basketball.add("France");
basketball.add("Russia");
expandableListDetail.put("CRICKET TEAMS", cricket);
expandableListDetail.put("FOOTBALL TEAMS", football);
expandableListDetail.put("BASKETBALL TEAMS", basketball);
return expandableListDetail;
}
}
Nel codice sopra, l’oggetto expandableListDetail è utilizzato per mappare le stringhe dell’intestazione del gruppo ai rispettivi figli utilizzando un ArrayList di stringhe. CustomExpandableListAdapter.java
package com.journaldev.expandablelistview;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Typeface;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseExpandableListAdapter;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class CustomExpandableListAdapter extends BaseExpandableListAdapter {
private Context context;
private List<String> expandableListTitle;
private HashMap<String, List<String>> expandableListDetail;
public CustomExpandableListAdapter(Context context, List<String> expandableListTitle,
HashMap<String, List<String>> expandableListDetail) {
this.context = context;
this.expandableListTitle = expandableListTitle;
this.expandableListDetail = expandableListDetail;
}
@Override
public Object getChild(int listPosition, int expandedListPosition) {
return this.expandableListDetail.get(this.expandableListTitle.get(listPosition))
.get(expandedListPosition);
}
@Override
public long getChildId(int listPosition, int expandedListPosition) {
return expandedListPosition;
}
@Override
public View getChildView(int listPosition, final int expandedListPosition,
boolean isLastChild, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
final String expandedListText = (String) getChild(listPosition, expandedListPosition);
if (convertView == null) {
LayoutInflater layoutInflater = (LayoutInflater) this.context
.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
convertView = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.list_item, null);
}
TextView expandedListTextView = (TextView) convertView
.findViewById(R.id.expandedListItem);
expandedListTextView.setText(expandedListText);
return convertView;
}
@Override
public int getChildrenCount(int listPosition) {
return this.expandableListDetail.get(this.expandableListTitle.get(listPosition))
.size();
}
@Override
public Object getGroup(int listPosition) {
return this.expandableListTitle.get(listPosition);
}
@Override
public int getGroupCount() {
return this.expandableListTitle.size();
}
@Override
public long getGroupId(int listPosition) {
return listPosition;
}
@Override
public View getGroupView(int listPosition, boolean isExpanded,
View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
String listTitle = (String) getGroup(listPosition);
if (convertView == null) {
LayoutInflater layoutInflater = (LayoutInflater) this.context.
getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
convertView = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.list_group, null);
}
TextView listTitleTextView = (TextView) convertView
.findViewById(R.id.listTitle);
listTitleTextView.setTypeface(null, Typeface.BOLD);
listTitleTextView.setText(listTitle);
return convertView;
}
@Override
public boolean hasStableIds() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isChildSelectable(int listPosition, int expandedListPosition) {
return true;
}
}
Questa classe estende BaseExpandableListAdapter e ne sovrascrive i metodi per fornire la vista per l’ExpandableListView. getView() inserisce i dati nella vista dell’elemento con l’indice fornito. MainActivity.java
package com.journaldev.expandablelistview;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ExpandableListAdapter;
import android.widget.ExpandableListView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
ExpandableListView expandableListView;
ExpandableListAdapter expandableListAdapter;
List<String> expandableListTitle;
HashMap<String, List<String>> expandableListDetail;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
expandableListView = (ExpandableListView) findViewById(R.id.expandableListView);
expandableListDetail = ExpandableListDataPump.getData();
expandableListTitle = new ArrayList<String>(expandableListDetail.keySet());
expandableListAdapter = new CustomExpandableListAdapter(this, expandableListTitle, expandableListDetail);
expandableListView.setAdapter(expandableListAdapter);
expandableListView.setOnGroupExpandListener(new ExpandableListView.OnGroupExpandListener() {
@Override
public void onGroupExpand(int groupPosition) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
expandableListTitle.get(groupPosition) + " List Expanded.",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
expandableListView.setOnGroupCollapseListener(new ExpandableListView.OnGroupCollapseListener() {
@Override
public void onGroupCollapse(int groupPosition) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
expandableListTitle.get(groupPosition) + " List Collapsed.",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
expandableListView.setOnChildClickListener(new ExpandableListView.OnChildClickListener() {
@Override
public boolean onChildClick(ExpandableListView parent, View v,
int groupPosition, int childPosition, long id) {
Toast.makeText(
getApplicationContext(),
expandableListTitle.get(groupPosition)
+ " -> "
+ expandableListDetail.get(
expandableListTitle.get(groupPosition)).get(
childPosition), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT
).show();
return false;
}
});
}
}
Nel codice sopra abbiamo implementato tutte le interfacce discusse in precedenza. Per semplicità, mostreremo solo un Toast con il nome dell’elemento o lo stato del gruppo per ogni clic. Tuttavia, questi possono essere facilmente modificati per eseguire qualsiasi altra operazione. Di seguito è riportata la nostra app con Android ExpandableListView in azione. 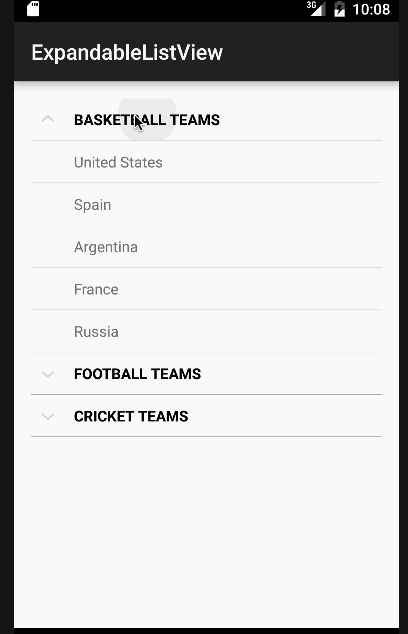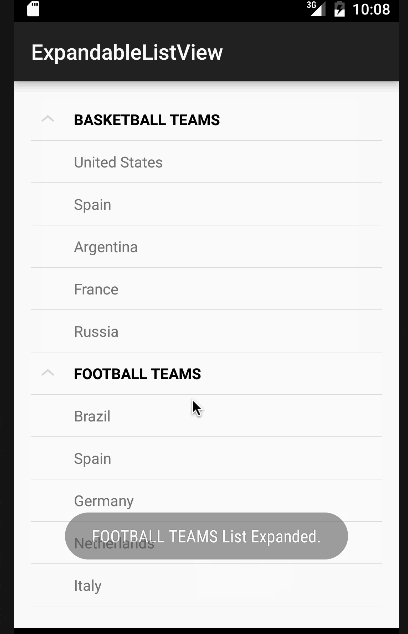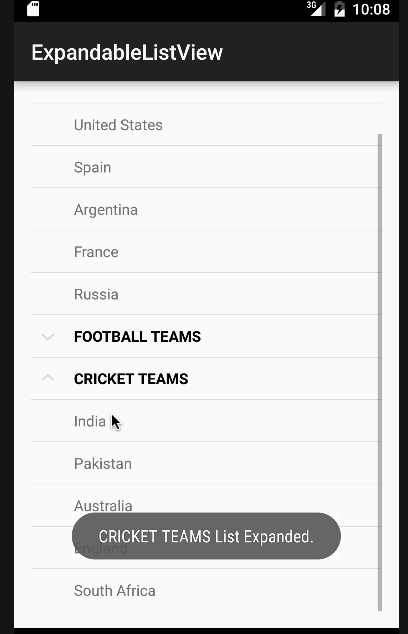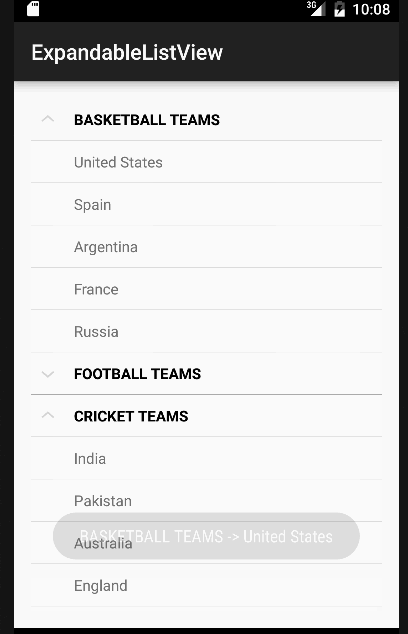 Nota: Gli ExpandableListViews sono scorrevoli per impostazione predefinita. Questo conclude il tutorial su Android ExpandableListView. Puoi scaricare il progetto finale Progetto Android ExpandableListView dal link sottostante.
Nota: Gli ExpandableListViews sono scorrevoli per impostazione predefinita. Questo conclude il tutorial su Android ExpandableListView. Puoi scaricare il progetto finale Progetto Android ExpandableListView dal link sottostante.
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/android-expandablelistview-example-tutorial













