Bienvenido al Tutorial de Ejemplo de Android ExpandableListView. En este tutorial implementaremos un ExpandableListView que se utiliza para agrupar datos de la lista por categorías. Es una especie de menú y submenús en un Android ListView.
Android ExpandableListView
Android ExpandableListView es una vista que muestra elementos en una lista de dos niveles que se desplaza verticalmente. A diferencia de un ListView, permite dos niveles que son grupos que se pueden expandir y contraer fácilmente tocándolos y sus respectivos elementos hijos. El adaptador ExpandableListViewAdapter en Android carga los datos en los elementos asociados con esta vista. A continuación, se presentan algunos métodos importantes que utiliza esta clase:
- setChildIndicator(Drawable): Se utiliza para mostrar un indicador al lado de cada elemento que representa el estado actual. Si el hijo es el último hijo de un grupo, se establecerá el estado
state_last - setGroupIndicator(Drawable): Se dibuja un indicador al lado del grupo que representa su estado, es decir, expandido o contraído. Si el grupo está vacío, se establecerá el estado
state_empty. Si el grupo está expandido, se establecerá el estadostate_expanded - getGroupView(): Devuelve la vista para el encabezado del grupo de la lista.
- getChildView() : Retorna la vista para el elemento secundario de la lista
Las interfaces notables implementadas por esta clase se detallan a continuación:
- ExpandableListView.OnChildClickListener : Se sobrescribe para implementar el método de devolución de llamada que se invoca cuando se hace clic en un hijo en la lista expandida
- ExpandableListView.OnGroupClickListener : Se sobrescribe para implementar el método de devolución de llamada que se invoca cuando se hace clic en el encabezado de un grupo en la lista expandida
- ExpandableListView.OnGroupCollapseListener : Se utiliza para notificar cuando se colapsa un grupo
- ExpandableListView.OnGroupExpandListener : Se utiliza para notificar cuando se expande un grupo
Estructura del Proyecto Android ExpandableListView
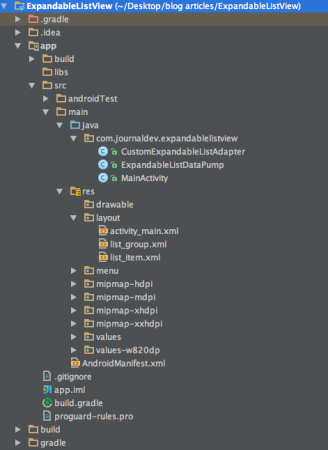 Este proyecto consta de tres clases.
Este proyecto consta de tres clases.
- A MainActivity that shows the layout with the ExpandableListView
- Un ExpandableListDataPump que representa datos aleatorios en una lista y asigna los datos de los elementos secundarios a los encabezados de grupo respectivos mediante un HashMap
- A CustomExpandableListAdapter which provides the MainActivity with the data from the ExpandableListDataPump class/li>
Código de ExpandableListView de Android
El diseño activity_main.xml consta de un ExpandableListView en un RelativeLayout como se muestra a continuación: activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="https://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<ExpandableListView
android:id="@+id/expandableListView"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:indicatorLeft="?android:attr/expandableListPreferredItemIndicatorLeft"
android:divider="@android:color/darker_gray"
android:dividerHeight="0.5dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
El android:indicatorLeft es el límite izquierdo para un indicador de elementos. Nota: No podemos usar el valor wrap_content para el atributo android:layout_height del ExpandableListView en XML a menos que el tamaño del padre esté estrictamente especificado. El diseño del encabezado de grupo de cada lista individual se muestra a continuación: list_group.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/listTitle"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingLeft="?android:attr/expandableListPreferredItemPaddingLeft"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:paddingTop="10dp"
android:paddingBottom="10dp" />
</LinearLayout>
El diseño de la fila de los elementos secundarios se muestra a continuación: list_item.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/expandedListItem"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingLeft="?android:attr/expandableListPreferredChildPaddingLeft"
android:paddingTop="10dp"
android:paddingBottom="10dp" />
</LinearLayout>
La clase ExpandableListDataPump está definida de la siguiente manera:
package com.journaldev.expandablelistview;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
public class ExpandableListDataPump {
public static HashMap<String, List<String>> getData() {
HashMap<String, List<String>> expandableListDetail = new HashMap<String, List<String>>();
List<String> cricket = new ArrayList<String>();
cricket.add("India");
cricket.add("Pakistan");
cricket.add("Australia");
cricket.add("England");
cricket.add("South Africa");
List<String> football = new ArrayList<String>();
football.add("Brazil");
football.add("Spain");
football.add("Germany");
football.add("Netherlands");
football.add("Italy");
List<String> basketball = new ArrayList<String>();
basketball.add("United States");
basketball.add("Spain");
basketball.add("Argentina");
basketball.add("France");
basketball.add("Russia");
expandableListDetail.put("CRICKET TEAMS", cricket);
expandableListDetail.put("FOOTBALL TEAMS", football);
expandableListDetail.put("BASKETBALL TEAMS", basketball);
return expandableListDetail;
}
}
En el código anterior, el objeto expandableListDetail se utiliza para asignar las cadenas de encabezado de grupo a sus respectivos elementos secundarios mediante un ArrayList de Strings. CustomExpandableListAdapter.java
package com.journaldev.expandablelistview;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Typeface;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseExpandableListAdapter;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class CustomExpandableListAdapter extends BaseExpandableListAdapter {
private Context context;
private List<String> expandableListTitle;
private HashMap<String, List<String>> expandableListDetail;
public CustomExpandableListAdapter(Context context, List<String> expandableListTitle,
HashMap<String, List<String>> expandableListDetail) {
this.context = context;
this.expandableListTitle = expandableListTitle;
this.expandableListDetail = expandableListDetail;
}
@Override
public Object getChild(int listPosition, int expandedListPosition) {
return this.expandableListDetail.get(this.expandableListTitle.get(listPosition))
.get(expandedListPosition);
}
@Override
public long getChildId(int listPosition, int expandedListPosition) {
return expandedListPosition;
}
@Override
public View getChildView(int listPosition, final int expandedListPosition,
boolean isLastChild, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
final String expandedListText = (String) getChild(listPosition, expandedListPosition);
if (convertView == null) {
LayoutInflater layoutInflater = (LayoutInflater) this.context
.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
convertView = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.list_item, null);
}
TextView expandedListTextView = (TextView) convertView
.findViewById(R.id.expandedListItem);
expandedListTextView.setText(expandedListText);
return convertView;
}
@Override
public int getChildrenCount(int listPosition) {
return this.expandableListDetail.get(this.expandableListTitle.get(listPosition))
.size();
}
@Override
public Object getGroup(int listPosition) {
return this.expandableListTitle.get(listPosition);
}
@Override
public int getGroupCount() {
return this.expandableListTitle.size();
}
@Override
public long getGroupId(int listPosition) {
return listPosition;
}
@Override
public View getGroupView(int listPosition, boolean isExpanded,
View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
String listTitle = (String) getGroup(listPosition);
if (convertView == null) {
LayoutInflater layoutInflater = (LayoutInflater) this.context.
getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
convertView = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.list_group, null);
}
TextView listTitleTextView = (TextView) convertView
.findViewById(R.id.listTitle);
listTitleTextView.setTypeface(null, Typeface.BOLD);
listTitleTextView.setText(listTitle);
return convertView;
}
@Override
public boolean hasStableIds() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isChildSelectable(int listPosition, int expandedListPosition) {
return true;
}
}
Esta clase extiende BaseExpandableListAdapter y anula los métodos de la clase base para proporcionar la vista para el ExpandableListView. getView() completa los datos en la vista del elemento con el índice dado. MainActivity.java
package com.journaldev.expandablelistview;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ExpandableListAdapter;
import android.widget.ExpandableListView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
ExpandableListView expandableListView;
ExpandableListAdapter expandableListAdapter;
List<String> expandableListTitle;
HashMap<String, List<String>> expandableListDetail;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
expandableListView = (ExpandableListView) findViewById(R.id.expandableListView);
expandableListDetail = ExpandableListDataPump.getData();
expandableListTitle = new ArrayList<String>(expandableListDetail.keySet());
expandableListAdapter = new CustomExpandableListAdapter(this, expandableListTitle, expandableListDetail);
expandableListView.setAdapter(expandableListAdapter);
expandableListView.setOnGroupExpandListener(new ExpandableListView.OnGroupExpandListener() {
@Override
public void onGroupExpand(int groupPosition) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
expandableListTitle.get(groupPosition) + " List Expanded.",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
expandableListView.setOnGroupCollapseListener(new ExpandableListView.OnGroupCollapseListener() {
@Override
public void onGroupCollapse(int groupPosition) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
expandableListTitle.get(groupPosition) + " List Collapsed.",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
expandableListView.setOnChildClickListener(new ExpandableListView.OnChildClickListener() {
@Override
public boolean onChildClick(ExpandableListView parent, View v,
int groupPosition, int childPosition, long id) {
Toast.makeText(
getApplicationContext(),
expandableListTitle.get(groupPosition)
+ " -> "
+ expandableListDetail.get(
expandableListTitle.get(groupPosition)).get(
childPosition), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT
).show();
return false;
}
});
}
}
En el código anterior hemos implementado todas las interfaces que fueron discutidas antes. Por simplicidad, solo mostraremos un Toast con el nombre del elemento o el estado del grupo por cada clic. Pero estos pueden ser fácilmente modificados para realizar cualquier otra operación. A continuación está nuestra aplicación con la vista de lista expandible de Android en acción. 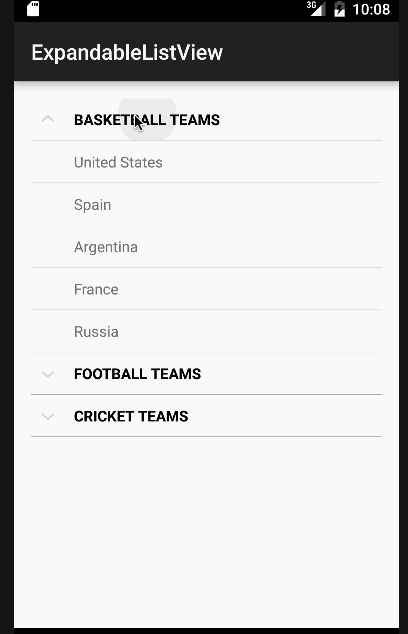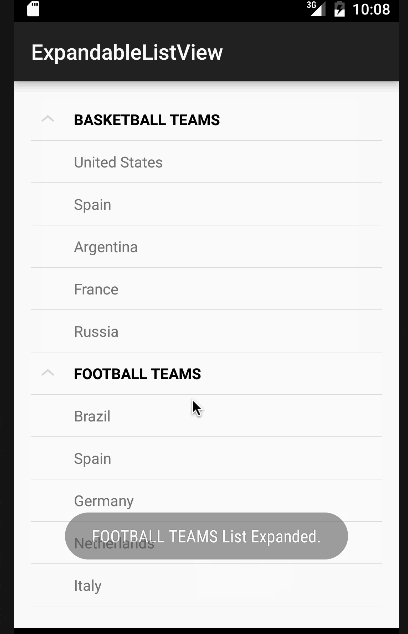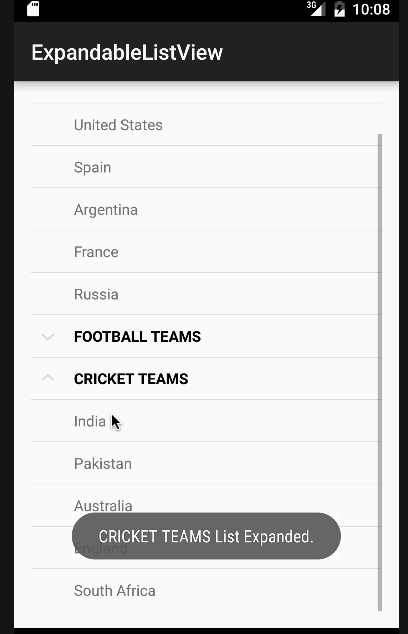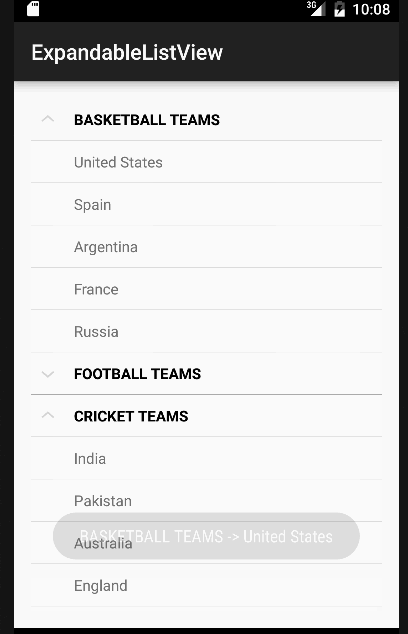 Nota: Las ExpandableListViews son desplazables por defecto. Esto marca el final del tutorial de Android ExpandableListView. Puedes descargar el Proyecto de Android ExpandableListView final desde el siguiente enlace.
Nota: Las ExpandableListViews son desplazables por defecto. Esto marca el final del tutorial de Android ExpandableListView. Puedes descargar el Proyecto de Android ExpandableListView final desde el siguiente enlace.
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/android-expandablelistview-example-tutorial













