Inheritance in java is one of the core concepts of Object-Oriented Programming. Java Inheritance is used when we have is-a relationship between objects. Inheritance in Java is implemented using extends keyword.
Inheritance in Java
Inheritance in Java is the method to create a hierarchy between classes by inheriting from other classes.
Java Inheritance is transitive – so if Sedan extends Car and Car extends Vehicle, then Sedan is also inherited from the Vehicle class. The Vehicle becomes the superclass of both Car and Sedan.
Inheritance is widely used in java applications, for example extending the Exception class to create an application-specific Exception class that contains more information such as error codes. For example NullPointerException.
Java Inheritance Example
Every class in java implicitly extends java.lang.Object class. So Object class is at the top level of inheritance hierarchy in java.
Let’s see how to implement inheritance in java with a simple example.
Superclass: Animal
package com.journaldev.inheritance;
public class Animal {
private boolean vegetarian;
private String eats;
private int noOfLegs;
public Animal(){}
public Animal(boolean veg, String food, int legs){
this.vegetarian = veg;
this.eats = food;
this.noOfLegs = legs;
}
public boolean isVegetarian() {
return vegetarian;
}
public void setVegetarian(boolean vegetarian) {
this.vegetarian = vegetarian;
}
public String getEats() {
return eats;
}
public void setEats(String eats) {
this.eats = eats;
}
public int getNoOfLegs() {
return noOfLegs;
}
public void setNoOfLegs(int noOfLegs) {
this.noOfLegs = noOfLegs;
}
}
The Animal is the base class here. Let’s create a Cat class that inherits from Animal class.
Subclass: Cat
package com.journaldev.inheritance;
public class Cat extends Animal{
private String color;
public Cat(boolean veg, String food, int legs) {
super(veg, food, legs);
this.color="White";
}
public Cat(boolean veg, String food, int legs, String color){
super(veg, food, legs);
this.color=color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
}
Notice that we are using extends keyword to implement inheritance in java.
Java Inheritance Test Program
Let’s write a simple test class to create a Cat object and use some of its methods.
package com.journaldev.inheritance;
public class AnimalInheritanceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat cat = new Cat(false, "milk", 4, "black");
System.out.println("Cat is Vegetarian?" + cat.isVegetarian());
System.out.println("Cat eats " + cat.getEats());
System.out.println("Cat has " + cat.getNoOfLegs() + " legs.");
System.out.println("Cat color is " + cat.getColor());
}
}
Output:
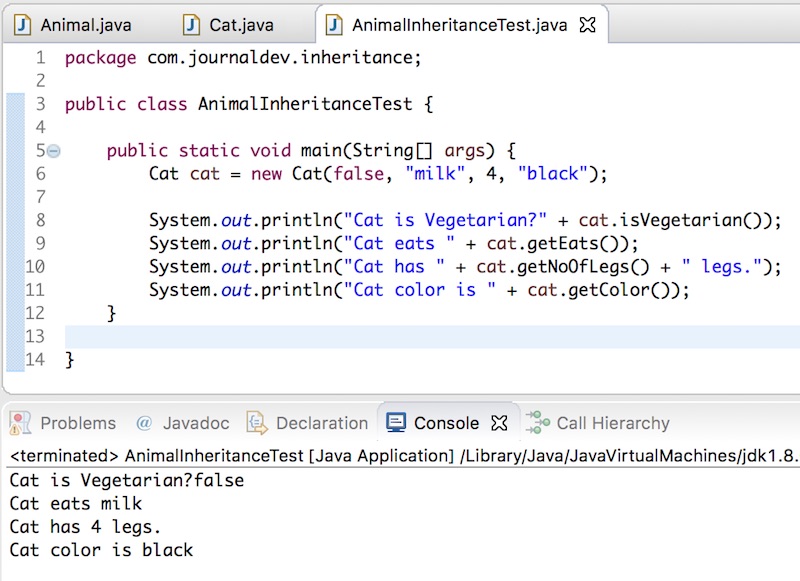
Cat class doesn’t have getEats() method but still, the program works because it’s inherited from Animal class.
Important Points
-
Code reuse is the most important benefit of inheritance because subclasses inherits the variables and methods of superclass.
-
Private members of superclass are not directly accessible to subclass. As in this example, Animal variable noOfLegs is not accessible to Cat class but it can be indirectly accessible via getter and setter methods.
-
Superclass members with default access is accessible to subclass ONLY if they are in same package.
-
Superclass constructors are not inherited by subclass.
-
If superclass doesn’t have default constructor, then subclass also needs to have an explicit constructor defined. Else it will throw compile time exception. In the subclass constructor, call to superclass constructor is mandatory in this case and it should be the first statement in the subclass constructor.
-
Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance, a subclass can extends only one class. Animal class is implicitly extending Object class and Cat is extending Animal class but due to java inheritance transitive nature, Cat class also extends Object class.
-
We can create an instance of subclass and then assign it to superclass variable, this is called upcasting. Below is a simple example of upcasting:
Cat c = new Cat(); //subclass instance Animal a = c; //upcasting, it's fine since Cat is also an Animal -
When an instance of Superclass is assigned to a Subclass variable, then it’s called downcasting. We need to explicitly cast this to Subclass. For example;
Cat c = new Cat(); Animal a = c; Cat c1 = (Cat) a; //explicit casting, works fine because "c" is actually of type CatNote that Compiler won’t complain even if we are doing it wrong, because of explicit casting. Below are some of the cases where it will throw
ClassCastExceptionat runtime.Dog d = new Dog(); Animal a = d; Cat c1 = (Cat) a; //ClassCastException at runtime Animal a1 = new Animal(); Cat c2 = (Cat) a1; //ClassCastException because a1 is actually of type Animal at runtime -
We can override the method of Superclass in the Subclass. However we should always annotate overridden method with @Override annotation. The compiler will know that we are overriding a method and if something changes in the superclass method, we will get a compile-time error rather than getting unwanted results at the runtime.
-
We can call the superclass methods and access superclass variables using super keyword. It comes handy when we have the same name variable/method in the subclass but we want to access the superclass variable/method. This is also used when Constructors are defined in the superclass and subclass and we have to explicitly call the superclass constructor.
-
We can use
instanceofinstruction to check the inheritance between objects, let’s see this with below example.
```
Cat c = new Cat();
Dog d = new Dog();
Animal an = c;
boolean flag = c instanceof Cat; //normal case, returns true
flag = c instanceof Animal; // returns true since c is-an Animal too
flag = an instanceof Cat; //returns true because a is of type Cat at runtime
flag = an instanceof Dog; //returns false for obvious reasons.
```
- We can’t extend Final classes in java.
- If you are not going to use Superclass in the code i.e your Superclass is just a base to keep reusable code then you can keep them as Abstract class to avoid unnecessary instantiation by client classes. It will also restrict the instance creation of base class.
Java Inheritance Video Tutorial
I have recently published two videos on YouTube explaining Inheritance in detail with sample programs, you should watch them below.
You can checkout more inheritance examples from our GitHub Repository.
Reference: Oracle Documentation
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/inheritance-java-example













