Android-Animation wird verwendet, um der Benutzeroberfläche ein ansprechendes Aussehen zu verleihen. Animationen in Android-Apps können durch XML oder Android-Code durchgeführt werden. In diesem Android-Animations-Tutorial verwenden wir XML-Codes, um Animationen in unsere Anwendung einzufügen.
Android-Animation
Animation in Android-Apps ist der Prozess der Erzeugung von Bewegung und Formänderung. Die grundlegenden Arten von Animationen, die wir in diesem Tutorial behandeln werden, sind:
- Fade-In-Animation
- Fade-Out-Animation
- Cross-Fading-Animation
- Blink-Animation
- Zoom-In-Animation
- Zoom-Out-Animation
- Rotate-Animation
- Move-Animation
- Slide-Up-Animation
- Slide-Down-Animation
- Bounce-Animation
- Sequential-Animation
- Together-Animation
Android-Animationsbeispiel XML
Wir erstellen ein Ressourcenverzeichnis unter dem res-Ordner mit dem Namen anim, um alle XML-Dateien mit der Animationslogik zu speichern. Nachfolgend finden Sie eine Beispieldatei im XML-Format, die den Logikcode für eine Android-Animation zeigt. sample_animation.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<scale xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_decelerate_interpolator"
android:duration="300"
android:fillAfter="true"
android:fromXScale="0.0"
android:fromYScale="0.0"
android:toXScale="1.0"
android:toYScale="1.0" />
-
android:interpolator : Es ist die Änderungsrate in der Animation. Wir können unsere eigenen Interpolatoren unter Verwendung der Zeit als Einschränkung definieren. Im obigen XML-Code wird ein integrierter Interpolator zugewiesen
-
android:dauer : Dauer der Animation, in der die Animation abgeschlossen sein soll. Hier sind es 300 ms. Dies ist in der Regel die ideale Dauer, um den Übergang auf dem Bildschirm anzuzeigen. Der Start und das Ende der Animation werden festgelegt durch:
android:vonTRANSFORMATION android:zuTRANSFORMATION -
TRANSFORMATION : ist die Transformation, die wir angeben möchten. In unserem Fall beginnen wir mit einer x- und y-Skalierung von 0 und enden mit einer x- und y-Skalierung von 1
-
android:fillAfter : Eigenschaft gibt an, ob die Ansicht am Ende der Animation sichtbar oder ausgeblendet sein soll. Wir haben sie im obigen Code sichtbar eingestellt. Wenn sie auf false gesetzt ist, ändert sich das Element nach der Animation in seinen vorherigen Zustand
-
android:startOffset : Dies ist die Wartezeit, bevor eine Animation beginnt. Diese Eigenschaft wird hauptsächlich verwendet, um mehrere Animationen nacheinander auszuführen
-
android:repeatMode : Dies ist nützlich, wenn Sie möchten, dass die Animation wiederholt wird
-
android:repeatCount : Dies definiert die Anzahl der Wiederholungen der Animation. Wenn wir diesen Wert auf unendlich setzen, wird die Animation unendlich oft wiederholt
Ladeanimation, wenn das UI-Widget geklickt wird
Unser Ziel ist es, eine Animation anzuzeigen, wenn auf ein Widget (sagen wir TextView) geklickt wird. Dafür müssen wir die Klasse Animation verwenden. Die XML-Datei, die die Animationslogik enthält, wird mithilfe der Klasse AnimationUtils durch Aufrufen der Funktion loadAnimation() geladen. Der folgende Ausschnitt zeigt diese Implementierung.
Animation animation;
animation = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.sample_animation);
Um die Animation zu starten, müssen wir die Funktion startAnimation() auf dem UI-Element aufrufen, wie im folgenden Ausschnitt gezeigt:
sampleTextView.startAnimation(animation);
Hier führen wir die Animation an einem TextView-Komponente durch, indem wir den Typ der Animation als Parameter übergeben.
Festlegen der Animationslistener
Dies ist nur erforderlich, wenn wir Ereignisse wie Start, Ende oder Wiederholung verfolgen möchten. Dafür muss die Aktivität AnimationListener implementieren, und die folgenden Methoden müssen überschrieben werden.
- onAnimationStart: Diese wird ausgelöst, sobald die Animation gestartet wurde.
- onAnimationEnd: Diese wird ausgelöst, sobald die Animation beendet ist.
- onAnimationRepeat: Diese wird ausgelöst, wenn die Animation wiederholt wird.
Android Animation Projektstruktur
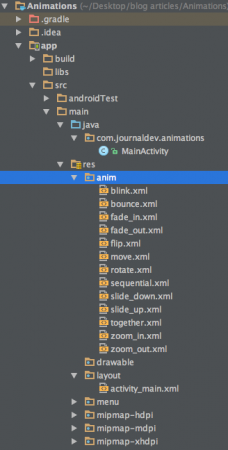 Wie Sie sehen können, haben wir das XML aller oben behandelten Hauptarten von Animationen eingefügt.
Wie Sie sehen können, haben wir das XML aller oben behandelten Hauptarten von Animationen eingefügt.
Beispiele für Android-Animationen XML-Code
Hier stelle ich Beispielscode für die meisten gängigen Android-Animationen bereit.
Einfadeanimation
fade_in.xml
<set xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:fillAfter="true" >
<alpha
android:duration="1000"
android:fromAlpha="0.0"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator"
android:toAlpha="1.0" />
</set>
Hier bezieht sich alpha auf die Deckkraft eines Objekts. Ein Objekt mit niedrigeren Alphawerten ist transparenter, während ein Objekt mit höheren Alphawerten weniger transparent, undurchsichtiger ist. Die Einfadeanimation besteht darin, den Alphawert von 0 auf 1 zu erhöhen.
Ausfadeanimation
fade_out.xml
<set xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:fillAfter="true" >
<alpha
android:duration="1000"
android:fromAlpha="1.0"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator"
android:toAlpha="0.0" />
</set>
Die Ausfadeanimation für Android ist genau das Gegenteil des Einfadens, bei dem wir den Alphawert von 1 auf 0 verringern müssen.
Kreuzüberblendungsanimation
Kreuzüberblendung führt eine Einblendungsanimation auf einem TextView aus, während ein anderer TextView ausgeblendet wird. Dies kann durch Verwendung von fade_in.xml und fade_out.xml auf den beiden TextViews erreicht werden. Der Code wird im MainActivity.java diskutiert.
Blinkanimation
blink.xml
<set xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<alpha android:fromAlpha="0.0"
android:toAlpha="1.0"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator"
android:duration="600"
android:repeatMode="reverse"
android:repeatCount="infinite"/>
</set>
Hier werden Einblenden und Ausblenden endlos im Rückwärtsmodus durchgeführt.
Hineinzoomenanimation
zoom_in.xml
<set xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:fillAfter="true" >
<scale
xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:duration="1000"
android:fromXScale="1"
android:fromYScale="1"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:toXScale="3"
android:toYScale="3" >
</scale>
</set>
Wir verwenden pivotX="50%" und pivotY="50%", um das Zoomen aus der Mitte des Elements durchzuführen.
Herauszoomenanimation
zoom_out.xml
<set xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:fillAfter="true" >
<scale
xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:duration="1000"
android:fromXScale="1.0"
android:fromYScale="1.0"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:toXScale="0.5"
android:toYScale="0.5" >
</scale>
</set>
Beachten Sie, dass android:from und android:to in den Dateien zoom_in.xml und zoom_out.xml entgegengesetzt sind.
Drehanimation
rotate.xml
<set xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<rotate android:fromDegrees="0"
android:toDegrees="360"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:duration="600"
android:repeatMode="restart"
android:repeatCount="infinite"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/cycle_interpolator"/>
</set>
A from/toDegrees tag is used here to specify the degrees and a cyclic interpolator is used.
Bewegungsanimation
move.xml
<set
xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/linear_interpolator"
android:fillAfter="true">
<translate
android:fromXDelta="0%p"
android:toXDelta="75%p"
android:duration="800" />
</set>
Einblenden nach oben Animation
slide_up.xml
<set xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:fillAfter="true" >
<scale
android:duration="500"
android:fromXScale="1.0"
android:fromYScale="1.0"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/linear_interpolator"
android:toXScale="1.0"
android:toYScale="0.0" />
</set>
Dies wird durch Festlegen von android:fromYScale=“1.0″ und android:toYScale=“0.0″ innerhalb des Tags scale erreicht.
Ausblenden nach unten Animation
slide_down.xml
<set xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:fillAfter="true">
<scale
android:duration="500"
android:fromXScale="1.0"
android:fromYScale="0.0"
android:toXScale="1.0"
android:toYScale="1.0" />
</set>
Dies ist genau das Gegenteil von slide_up.xml.
bounce.xml
<set xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:fillAfter="true"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/bounce_interpolator">
<scale
android:duration="500"
android:fromXScale="1.0"
android:fromYScale="0.0"
android:toXScale="1.0"
android:toYScale="1.0" />
</set>
Hier wird der Bounce-Interpolator verwendet, um die Animation im Hüpf-Stil zu vervollständigen.
sequential.xml
<set xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:fillAfter="true"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/linear_interpolator" >
<!-- Move -->
<translate
android:duration="800"
android:fillAfter="true"
android:fromXDelta="0%p"
android:startOffset="300"
android:toXDelta="75%p" />
<translate
android:duration="800"
android:fillAfter="true"
android:fromYDelta="0%p"
android:startOffset="1100"
android:toYDelta="70%p" />
<translate
android:duration="800"
android:fillAfter="true"
android:fromXDelta="0%p"
android:startOffset="1900"
android:toXDelta="-75%p" />
<translate
android:duration="800"
android:fillAfter="true"
android:fromYDelta="0%p"
android:startOffset="2700"
android:toYDelta="-70%p" />
<!-- Rotate 360 degrees -->
<rotate
android:duration="1000"
android:fromDegrees="0"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/cycle_interpolator"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:startOffset="3800"
android:repeatCount="infinite"
android:repeatMode="restart"
android:toDegrees="360" />
</set>
Hier wird ein unterschiedliches android:startOffset von den Übergängen verwendet, um sie sequenziell zu halten.
together.xml
<set xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:fillAfter="true"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/linear_interpolator" >
<!-- Move -->
<scale
xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:duration="4000"
android:fromXScale="1"
android:fromYScale="1"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:toXScale="4"
android:toYScale="4" >
</scale>
<!-- Rotate 180 degrees -->
<rotate
android:duration="500"
android:fromDegrees="0"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:repeatCount="infinite"
android:repeatMode="restart"
android:toDegrees="360" />
</set>
Hier wird android:startOffset entfernt, um sie gleichzeitig stattfinden zu lassen.
Code
Das Layout activity_main.xml besteht aus einem ScrollView und einem RelativeLayout (wir werden dies in einem späteren Tutorial besprechen), in dem jeder Animations typ auf den Text über ihre jeweiligen Schaltflächen aufgerufen wird. Die XML-Datei wird unten gezeigt: activity_main.xml
<ScrollView xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnFadeIn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="Fade In" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Fade In"
android:id="@+id/txt_fade_in"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btnFadeIn"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/txt_fade_out"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/txt_fade_out" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnFadeOut"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_below="@id/btnFadeIn"
android:text="Fade Out" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnCrossFade"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_below="@id/btnFadeOut"
android:text="Cross Fade" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Cross Fade In"
android:id="@+id/txt_out"
android:visibility="gone"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_alignTop="@+id/txt_in"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/txt_in"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/txt_in" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnBlink"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_below="@id/btnCrossFade"
android:text="Blink" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnZoomIn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_below="@id/btnBlink"
android:text="Zoom In" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Blink"
android:id="@+id/txt_blink"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btnBlink"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/txt_zoom_in"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/txt_zoom_in" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnZoomOut"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_below="@id/btnZoomIn"
android:text="Zoom Out" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnRotate"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_below="@id/btnZoomOut"
android:text="Rotate" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnMove"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_below="@id/btnRotate"
android:text="Move" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnSlideUp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_below="@id/btnMove"
android:text="Slide Up" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Fade Out"
android:id="@+id/txt_fade_out"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btnFadeOut"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/txt_in"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/txt_in" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnSlideDown"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_below="@id/btnSlideUp"
android:text="Slide Down" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnBounce"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_below="@id/btnSlideDown"
android:text="Bounce" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnSequential"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_below="@id/btnBounce"
android:text="Sequential Animation" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnTogether"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/btnSequential"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="Together Animation" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Cross Fade Out"
android:id="@+id/txt_in"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btnCrossFade"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/txt_blink"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/txt_blink" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Zoom In"
android:id="@+id/txt_zoom_in"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btnZoomIn"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/txt_zoom_out"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/txt_zoom_out" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Zoom Out"
android:id="@+id/txt_zoom_out"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btnZoomOut"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/btnSequential"
android:layout_toEndOf="@+id/btnSequential" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Rotate"
android:id="@+id/txt_rotate"
android:layout_above="@+id/btnMove"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/btnSequential"
android:layout_toEndOf="@+id/btnSequential" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Move"
android:id="@+id/txt_move"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btnMove"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/txt_slide_up"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/txt_slide_up" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Slide Up"
android:id="@+id/txt_slide_up"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btnSlideUp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/btnSequential"
android:layout_toEndOf="@+id/btnSequential" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Slide Down"
android:id="@+id/txt_slide_down"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btnSlideDown"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/txt_slide_up"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/txt_slide_up" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Bounce"
android:id="@+id/txt_bounce"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btnBounce"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/txt_slide_down"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/txt_slide_down" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Sequential"
android:id="@+id/txt_seq"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btnSequential"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/txt_bounce"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/txt_bounce" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Together"
android:id="@+id/txt_tog"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btnTogether"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/btnSequential"
android:layout_toEndOf="@+id/btnSequential" />
</RelativeLayout>
</ScrollView>
Zusammenfassend gesagt, ein RelativeLayout ordnet UI-Komponenten relativ zueinander an. Die Datei MainActivity.java enthält die onClick-Listener für jede Taste, die mit ihrem Animationstyp zusammenhängt. Der Quellcode ist unten angegeben.
package com.journaldev.animations;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.AnimationUtils;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Button btnFadeIn, btnFadeOut, btnCrossFade, btnBlink, btnZoomIn,
btnZoomOut, btnRotate, btnMove, btnSlideUp, btnSlideDown,
btnBounce, btnSequential, btnTogether;
Animation animFadeIn,animFadeOut,animBlink,animZoomIn,animZoomOut,animRotate
,animMove,animSlideUp,animSlideDown,animBounce,animSequential,animTogether,animCrossFadeIn,animCrossFadeOut;
TextView txtFadeIn,txtFadeOut,txtBlink,txtZoomIn,txtZoomOut,txtRotate,txtMove,txtSlideUp,
txtSlideDown,txtBounce,txtSeq,txtTog,txtIn,txtOut;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btnFadeIn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnFadeIn);
btnFadeOut = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnFadeOut);
btnCrossFade = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnCrossFade);
btnBlink = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnBlink);
btnZoomIn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnZoomIn);
btnZoomOut = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnZoomOut);
btnRotate = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnRotate);
btnMove = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnMove);
btnSlideUp = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnSlideUp);
btnSlideDown = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnSlideDown);
btnBounce = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnBounce);
btnSequential = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnSequential);
btnTogether = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnTogether);
txtFadeIn=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_fade_in);
txtFadeOut=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_fade_out);
txtBlink=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_blink);
txtZoomIn=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_zoom_in);
txtZoomOut=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_zoom_out);
txtRotate=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_rotate);
txtMove=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_move);
txtSlideUp=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_slide_up);
txtSlideDown=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_slide_down);
txtBounce=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_bounce);
txtSeq=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_seq);
txtTog=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_tog);
txtIn=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_in);
txtOut=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_out);
animFadeIn = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.fade_in);
animFadeIn = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.fade_in);
// Einblenden
btnFadeIn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
txtFadeIn.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
txtFadeIn.startAnimation(animFadeIn);
}
});
animFadeOut = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.fade_out);
// Ausblenden
btnFadeOut.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
txtFadeOut.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
txtFadeOut.startAnimation(animFadeOut);
}
});
animCrossFadeIn = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.fade_in);
animCrossFadeOut = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.fade_out);
// Überblenden
btnCrossFade.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
txtOut.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
// Einblendanimation starten
txtOut.startAnimation(animCrossFadeIn);
// Ausblendanimation starten
txtIn.startAnimation(animCrossFadeOut);
}
});
animBlink = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.blink);
// Blinken
btnBlink.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
txtBlink.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
txtBlink.startAnimation(animBlink);
}
});
animZoomIn = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.zoom_in);
// Hineinzoomen
btnZoomIn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
txtZoomIn.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
txtZoomIn.startAnimation(animZoomIn);
}
});
animZoomOut = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.zoom_out);
// Herauszoomen
btnZoomOut.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
txtZoomOut.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
txtZoomOut.startAnimation(animZoomOut);
}
});
animRotate = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.rotate);
// Rotate
btnRotate.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
txtRotate.startAnimation(animRotate);
}
});
animMove = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.move);
// Move
btnMove.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
txtMove.startAnimation(animMove);
}
});
animSlideUp = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.slide_up);
// Nach oben gleiten
btnSlideUp.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
txtSlideUp.startAnimation(animSlideUp);
}
});
animSlideDown = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.slide_down);
// Nach unten gleiten
btnSlideDown.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
txtSlideDown.startAnimation(animSlideDown);
}
});
animBounce = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.bounce);
// Nach unten gleiten
btnBounce.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
txtBounce.startAnimation(animBounce);
}
});
animSequential = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.sequential);
// Sequential
btnSequential.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
txtSeq.startAnimation(animSequential);
}
});
animTogether = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(),
R.anim.together);
// Together
btnTogether.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
txtTog.startAnimation(animTogether);
}
});
}
}
Wie zuvor besprochen, wird jede TextView-Animation durch Aufrufen des entsprechenden Animationsobjekts gestartet, in dem die Animationslogik durch die Methode AnimationUtils.loadAnimation() geladen wird. Die CrossFade-Animation besteht aus zwei TextViews, bei der eine ausgeblendet und die andere eingeblendet wird. Unten ist ein kurzes Video zu sehen, das alle Animationen in unserer Anwendung zeigt. 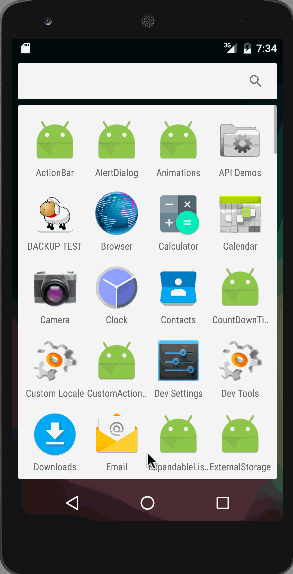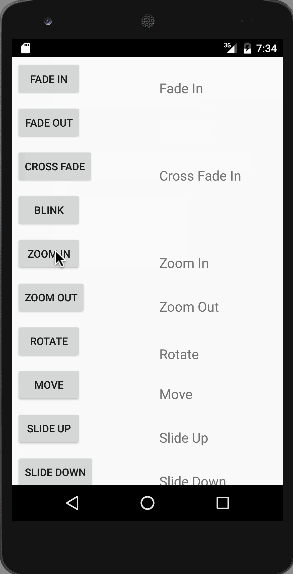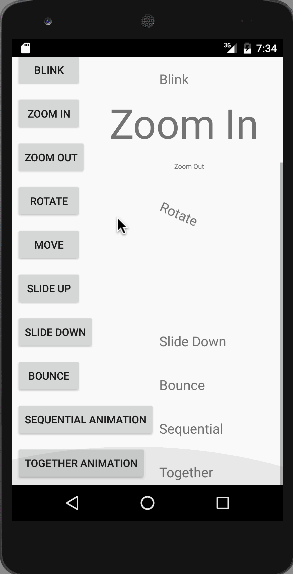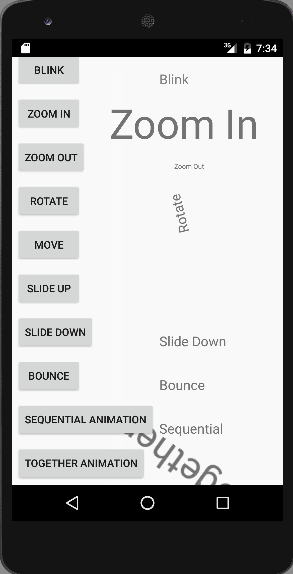 Die gemeinsame Animation ist im obigen Bild zu sehen. Beachten Sie, dass diese Animationen auf einem Emulator nicht flüssig ablaufen, daher wird empfohlen, die Anwendung auf einem normalen Gerät auszuführen. Damit endet das Beispiel-Tutorial zur Android-Animation. Sie können das Android-Animationsbeispielprojekt über den folgenden Link herunterladen.
Die gemeinsame Animation ist im obigen Bild zu sehen. Beachten Sie, dass diese Animationen auf einem Emulator nicht flüssig ablaufen, daher wird empfohlen, die Anwendung auf einem normalen Gerät auszuführen. Damit endet das Beispiel-Tutorial zur Android-Animation. Sie können das Android-Animationsbeispielprojekt über den folgenden Link herunterladen.
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/android-animation-example













