Pythonのビット演算子は、整数に対してビット演算を行うために使用されます。整数はバイナリ形式に変換され、ビットごとに演算が行われるため、ビット演算子と呼ばれています。Pythonのビット演算子は整数に対してのみ機能し、最終的な出力は10進数の形式で返されます。Pythonのビット演算子は、バイナリ演算子とも呼ばれています。
Pythonのビット演算子
Pythonには6つのビット演算子があります。以下の表はそれについての短い詳細を提供しています。
| Bitwise Operator | Description | Simple Example |
|---|---|---|
| & | Bitwise AND Operator | 10 & 7 = 2 |
| Bitwise OR Operator | ||
| ^ | Bitwise XOR Operator | 10 ^ 7 = 13 |
| ~ | Bitwise Ones’ Compliment Operator | ~10 = -11 |
| << | Bitwise Left Shift operator | 10<<2 = 40 |
| >> | Bitwise Right Shift Operator | 10>>1 = 5 |
それでは、これらの演算子を一つずつ見て、どのように機能するかを理解してみましょう。
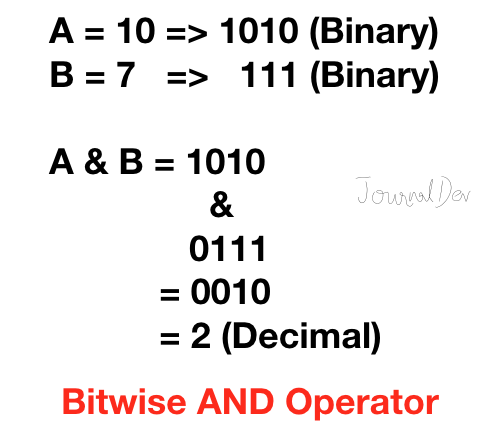
1. ビットAND演算子
PythonのビットAND演算子は、両方のビットが1の場合は1を返し、それ以外の場合は0を返します。
>>> 10&7
2
>>>
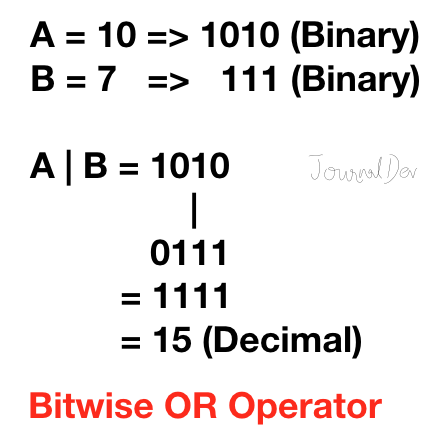
2. ビットOR演算子
PythonのビットOR演算子は、どちらかのビットが1の場合は1を返します。両方のビットが0の場合は0を返します。
>>> 10|7
15
>>>
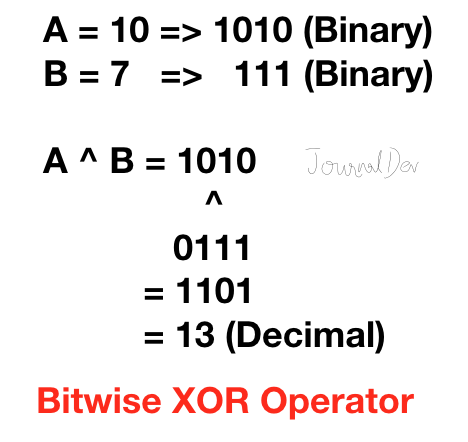
3. ビット単位のXOR演算子
Pythonのビット単位のXOR演算子は、1つのビットが0であり、もう1つのビットが1の場合に1を返します。両方のビットが0または1の場合は、0を返します。
>>> 10^7
13
>>>
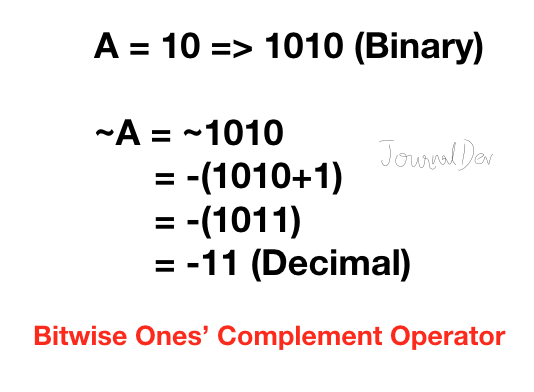
4. ビット単位の1の補数演算子
Pythonの1の補数は、数値 ‘A’ の補数であり、-(A+1)に等しいです。
>>> ~10
-11
>>> ~-10
9
>>>
5. ビット単位の左シフト演算子
Pythonのビット単位の左シフト演算子は、左のオペランドのビットを右のオペランドで指定された回数だけ左側にシフトします。単純に言えば、2進数は末尾に0が追加されます。
>>> 10 << 2
40
>>>

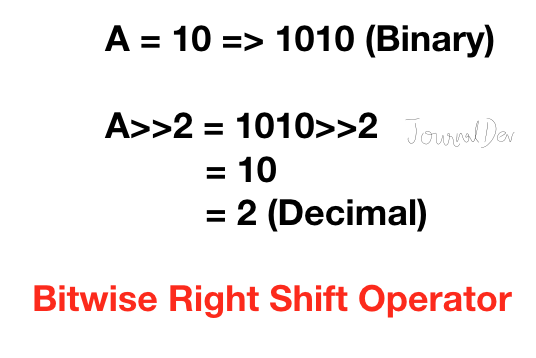
6. ビット単位の右シフト演算子
Pythonの右シフト演算子は、左シフト演算子とまったく逆です。つまり、左側のオペランドのビットが指定された回数右側に移動します。簡単に言うと、右側のビットが削除されます。
>>> 10 >> 2
2
>>>
Pythonのビット演算子オーバーローディング
Pythonは演算子のオーバーローディングをサポートしています。カスタムオブジェクトでビット演算子をサポートするために実装できるさまざまな方法があります。
| Bitwise Operator | Method to Implement |
|---|---|
| & | __and__(self, other) |
| ^ | __xor__(self, other) |
| ~ | __invert__(self) |
| << | __lshift__(self, other) |
| >> | __rshift__(self, other) |
以下は、カスタムオブジェクトのビット演算子のオーバーローディングの例です。
class Data:
id = 0
def __init__(self, i):
self.id = i
def __and__(self, other):
print('Bitwise AND operator overloaded')
if isinstance(other, Data):
return Data(self.id & other.id)
else:
raise ValueError('Argument must be object of Data')
def __or__(self, other):
print('Bitwise OR operator overloaded')
if isinstance(other, Data):
return Data(self.id | other.id)
else:
raise ValueError('Argument must be object of Data')
def __xor__(self, other):
print('Bitwise XOR operator overloaded')
if isinstance(other, Data):
return Data(self.id ^ other.id)
else:
raise ValueError('Argument must be object of Data')
def __lshift__(self, other):
print('Bitwise Left Shift operator overloaded')
if isinstance(other, int):
return Data(self.id << other)
else:
raise ValueError('Argument must be integer')
def __rshift__(self, other):
print('Bitwise Right Shift operator overloaded')
if isinstance(other, int):
return Data(self.id >> other)
else:
raise ValueError('Argument must be integer')
def __invert__(self):
print('Bitwise Ones Complement operator overloaded')
return Data(~self.id)
def __str__(self):
return f'Data[{self.id}]'
d1 = Data(10)
d2 = Data(7)
print(f'd1&d2 = {d1&d2}')
print(f'd1|d2 = {d1|d2}')
print(f'd1^d2 = {d1^d2}')
print(f'd1<<2 = {d1<<2}')
print(f'd1>>2 = {d1>>2}')
print(f'~d1 = {~d1}')
出力:
Bitwise AND operator overloaded
d1&d2 = Data[2]
Bitwise OR operator overloaded
d1|d2 = Data[15]
Bitwise XOR operator overloaded
d1^d2 = Data[13]
Bitwise Left Shift operator overloaded
d1<<2 = Data[40]
Bitwise Right Shift operator overloaded
d1>>2 = Data[2]
Bitwise Ones Complement operator overloaded
~d1 = Data[-11]
新しい文字列フォーマットに慣れていない場合は、Pythonのf-stringsを読んでください。
サマリー
Pythonのビット演算子は主に数学的な計算で使用されます。カスタムクラスの実装でもビット演算子をサポートするための特定の方法を実装することができます。
Source:
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/python-bitwise-operators













